7.9 KiB
Firmware Dumping
Flash Memory Types
- NOR Flash (SOIC8 package)
- SPI Flash
- Mostly error "Fault-free" memory
- Used for embedded device that need fast execution, but low storage capacity
- NAND Flash (TSOP48 package)
- eMMC Flash (BGA{153} package)
- UFS Universal Flash Storage
Flash a new firmware into the microcontroller
-
Using avrdudes/avrdude
# send raw data firmware $ avrdude -p m328p -c usbasp -P /dev/ttyUSB0 -b 9600 -U flash:w:flash_raw.bin # send ihex firmware $ avrdude -c arduino -p atmega328p -P /dev/ttyUSB* -b115200 -u -V -U flash:w:CHALLENGE.hex $ avrdude -c usbasp -p m328p -F -U flash:r:dump.hex:i # default $ avrdude -c usbasp -p m328p -C /etc/avrdude.conf -U flash:w:hardcodedPassword.ino.arduino_standard.hex -
Using raspberrypi/picotool
# extension indicates the type (bin, uf2) picotool load firmware.bin
Dump flash using debug port
-
Using avrdudes/avrdude
$ avrdude -p m328p -c usbasp -P /dev/ttyUSB0 -b 9600 -U flash:r:flash_raw.bin:r $ avrdude -p m328p -c arduino -P /dev/ttyACM0 -b 115200 -U flash:r:flash_raw.bin:r $ avrdude -p atmega328p -c arduino -P/dev/ttyACM0 -b 115200 -D -U flash:r:program.bin:r -F -v -
Using openocd-org/openocd
- Determine code space in the microcontroller (for example nRF51822 - Micro:bit), save as
dump_img.cfg:init reset init halt dump_image image.bin 0x00000000 0x00040000 exit - Dump with openocd
sudo openocd -f /home/maki/tools/hardware/openocd/tcl/interface/stlink-v2-1.cfg -f /home/maki/tools/hardware/openocd/tcl/target/nrf51.cfg -f dump_fw.cfg
- Determine code space in the microcontroller (for example nRF51822 - Micro:bit), save as
-
Using raspberrypi/picotool
- Build PicoTool, you will need the pico-sdk
# PicoSDK git clone https://github.com/raspberrypi/pico-sdk.git cd pico-sdk git submodule update --init # Picotool cd .. git clone https://github.com/raspberrypi/picotool.git cd picotool mkdir build cd build cmake -DPICO_SDK_PATH=../pico-sdk .. make - Dump the program or the whole flash memory
sudo ./picotool save -F /tmp/out.bin Saving file: [==============================] 100% Wrote 73312 bytes to /tmp/out.bin sudo ./picotool save --all -F /tmp/out2.bin Saving file: [==============================] 100% Wrote 2097152 bytes to /tmp/out2.bin
- Build PicoTool, you will need the pico-sdk
Dump Flash via SPI
-
Using flashrom/flashroom
sudo apt-get install build-essential pciutils usbutils libpci-dev libusb-dev libftdi1 libftdi-dev zlib1g-dev subversion libusb-1.0-0-dev svn co svn://flashrom.org/flashrom/trunk flashrom cd flashrom make flashrom -p ft232_spi:type:232h -r spidump.bin flashrom -p linux_spi:dev=/dev/spidev0.0,spispeed=512 -r spi_dump.bin flashrom -p serprog:dev=/dev/ttyACM0,spispeed=160k -r dump_spi.bin -c "MX25L6406E/MX25L6408E" -
Using HydraBus: hydrabus/hydrafw/hydra_spi_dump.py
./hydra_spi_dump.py firmware.bin 1024 0x000000 fast
Convert ihex to elf
The Intel HEX is a transitional file format for microcontrollers, (E)PROMs, and other devices. The documentation states that HEXs can be converted to binary files and programmed into a configuration device.
Each line in the ihex file starts with :
- a colon :
- followed by ONE BYTE = record length
- followed by TWO BYTES = offset to load
- followed by ONE BYTE = Record Type
- Last BYTE in the line = Checksum
Convert .hex(ihex format) to .elf file with avr-objcopy or with an online tool http://matrixstorm.com
$ avr-objcopy -I ihex -O elf32-avr dump.hex dump.elf
# or
$ objcopy -I ihex chest.hex -O binary chest.bin ; xxd chest.bin
Alternative with Python bincopy
import bincopy
import sys
f = bincopy.BinFile()
f.add_ihex_file(sys.argv[1])
print(f.as_binary())
Quick strings on .hex
cat defaultPassword.ino.arduino_standard.hex | tr -d ":" | tr -d "\n" | xxd -r -p | strings
Inspect the assembly with avr-objdump -m avr -D chest.hex.
Emulate : qemu-system-avr -S -s -nographic -serial tcp::5678,server=on,wait=off -machine uno -bios chest.bin
Explore firmware
-
$ strings file.bin $ strings -e l file.bin The strings -e flag specifies the encoding of the characters. -el specifies little-endian characters 16-bits wide (e.g. UTF-16) $ strings -tx file.bin The -t flag will return the offset of the string within the file. -tx will return it in hex format, T-to in octal and -td in decimal. -
$ dd if=firmware.bin of=firmware.chunk bs=1 skip=$((0x200)) count=$((0x400-0x200)) If we wanted to run it a little faster, we could increase the block size: $ dd if=firmware.bin of=firmware.chunk bs=$((0x100)) skip=$((0x200/0x100)) count=$(((0x400-0x200)/0x100)) -
$ binwalk -Me file.bin $ binwalk -Y dump.elf DECIMAL HEXADECIMAL DESCRIPTION -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 3708 0xE7C ARM executable code, 16-bit (Thumb), little endian, at least 522 valid instructions -
sudo unsquashfs -f -d /media/seagate /tmp/file.squashfs -
docker run --rm --pull always -v /path/to/extract-dir/on/host:/data/output -v /path/to/files/on/host:/data/input ghcr.io/onekey-sec/unblob:latest /data/input/path/to/file docker run --rm --pull always ghcr.io/onekey-sec/unblob:latest --help -
onekey-sec/jefferson - JFFS2 filesystem extraction tool
pip install jefferson jefferson filesystem.img -d outdir jefferson file.jffs2 -d jffs2
Write new firmware
-
Repack firmware
mksquashfs4 squashfs-root myrootfs {options} dd if=myrootfs of=dump/bin bs=1 seek=<offset> conv=notrunc -
Flashrom write
flashrom -p ft2232_spi:type=232H -w dump.bin
Type of firmware
SREC- Motorola S-Record : All S-record file lines start with a capital S.Intel HEXlines all start with a colon.TI-TXTis a Texas Instruments format, usually for the MSP430 series. Memory addresses are prepended with an @, and data is represented in hex.RawNAND dumps
Check entropy
High entropy = probably encrypted (or compressed). Low entropy = probably not
$ binwalk -E fw
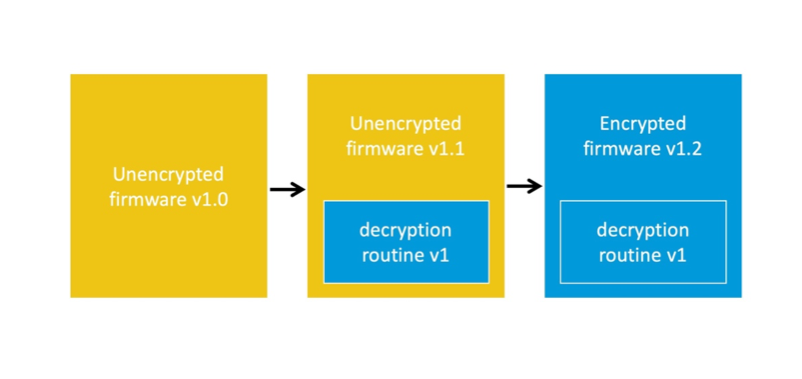
Encrypted firmware
Over-the-air updates
TODO