Github Action - Markdown Linting for Push and PR
parent
4c3f9e454b
commit
a29cfc4cd1
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,6 @@
|
|||
{
|
||||
"MD013": false,
|
||||
"ul-indent": {
|
||||
"indent": 4
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
|
|||
name: check-markdown
|
||||
on: [push, pull_request]
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
lint:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
fetch-depth: 0
|
||||
|
||||
- uses: tj-actions/changed-files@v45
|
||||
id: changed-files
|
||||
with:
|
||||
files: '**/*.md'
|
||||
separator: ","
|
||||
|
||||
- uses: DavidAnson/markdownlint-cli2-action@v17
|
||||
if: steps.changed-files.outputs.any_changed == 'true'
|
||||
with:
|
||||
globs: ${{ steps.changed-files.outputs.all_changed_files }}
|
||||
separator: ","
|
||||
config: ./.github/.markdownlint.json
|
||||
|
|
@ -12,7 +12,6 @@ Generally, the line is held high (at a logical 1 value) while UART is in idle st
|
|||
|
||||
We call the most common configuration **8N1**: eight data bits, no parity, and 1 stop bit.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Identifying UART ports
|
||||
|
||||
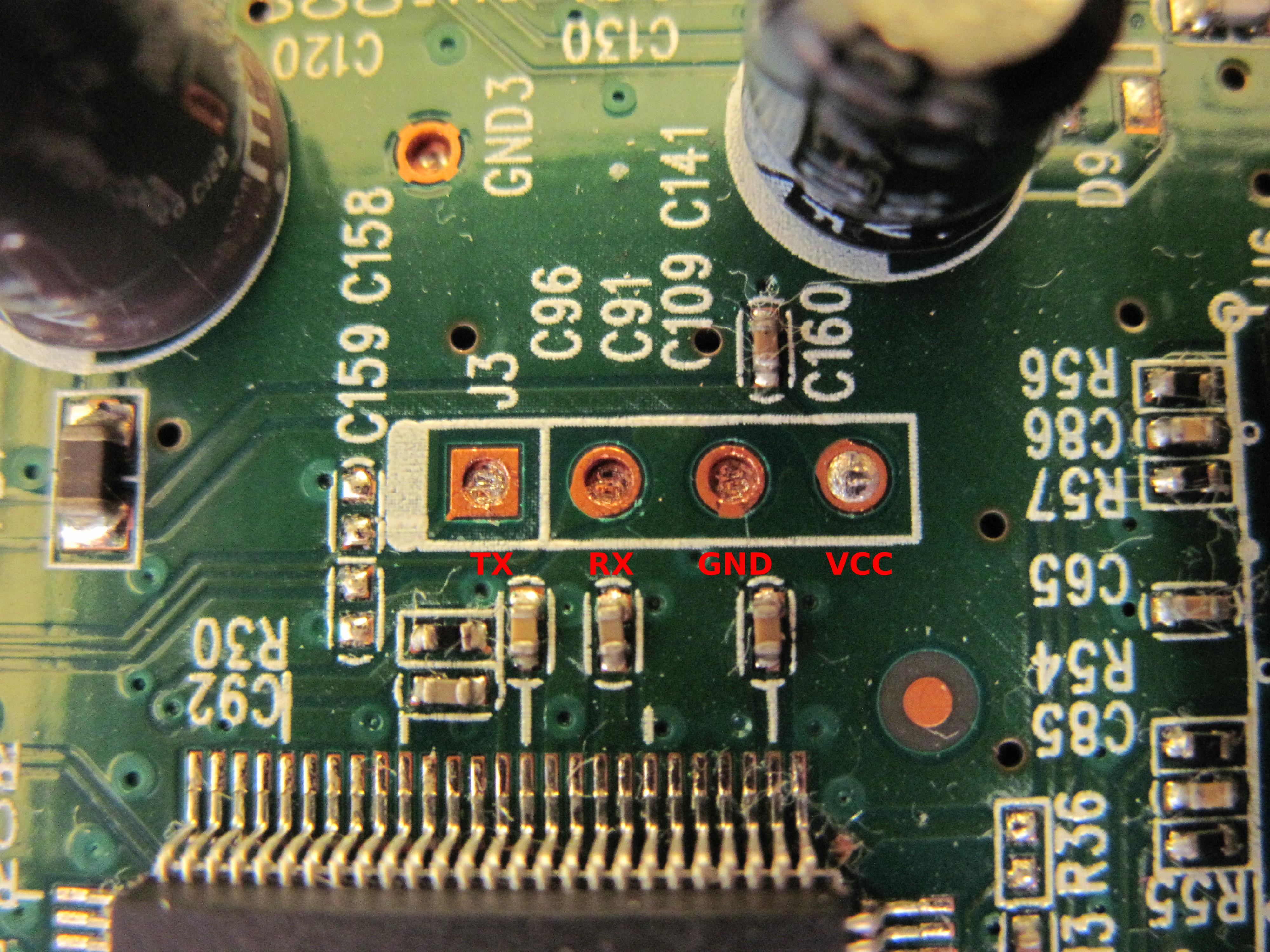
A UART pinout has **four** ports:
|
||||
|
|
@ -22,14 +21,15 @@ A UART pinout has **four** ports:
|
|||
* **VCC** (Voltage)
|
||||
* **GND** (Ground)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
To find UART there are multiple solutions:
|
||||
|
||||
* Search the Internet
|
||||
* Check the PCB for pin labels
|
||||
* Find likely candidates
|
||||
* Using a multimeter
|
||||
* Using a logic analyzer
|
||||
* Using a multimeter
|
||||
* Using a logic analyzer
|
||||
* Follow PCB traces (almost always impossible)
|
||||
|
||||
Keep in mind that some devices **emulate** UART ports by programming the General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO) pins if there isn't enough space on the board for dedicated hardware UART pins.
|
||||
|
|
@ -62,27 +62,24 @@ If you've already identified the rest of the UART pins, the nearby fourth pin is
|
|||
|
||||
Otherwise, you can identify it because it has the lowest voltage fluctuation and lowest overall value of all the UART pins.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Using a logic analyzer
|
||||
|
||||
A logic analyzer is an electronic instrument that captures and displays multiple signals from a digital system or digital circuit.
|
||||
|
||||
To find the UART pins we will connect the pins to a logic analyzer and look for data being transmitted.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Hardware setup
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure any system you're testing is **powered off** when you connect the logic analyzer's probes to it **to avoid short-circuiting**.
|
||||
|
||||
* Connect the suspected TX pin to any channel of the logic analyzer.
|
||||
* Connect one of your logic analyzer's GND pins to the PCB that you're testing GND pins so they **share a common ground**.
|
||||
|
||||
* Connect the suspected TX pin to any channel of the logic analyzer.
|
||||
* Connect one of your logic analyzer's GND pins to the PCB that you're testing GND pins so they **share a common ground**.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Software setup
|
||||
|
||||
##### PulseView / Sigrok
|
||||
|
||||
:warning: In order to make Pulseview work on Windows host, you have to use Zadig driver: https://zadig.akeo.ie/
|
||||
:warning: In order to make Pulseview work on Windows host, you have to use Zadig driver: <https://zadig.akeo.ie/>
|
||||
|
||||
* Click run on the top left corner in order to start the capture
|
||||
* Once you get UART communication, you can add a "protocol decoder"
|
||||
|
|
@ -112,27 +109,28 @@ This setup is for **Saleae-based logic analyzer** if you use a different one, re
|
|||
* Save the configurations.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to modify the speed and the duration:
|
||||
|
||||
* As a rule, you should sample digital signals **at least four times faster than their bandwidth**.
|
||||
* With serial communications, which are generally very slow, a **50 kS/s** sampling rate is more than enough, although sampling faster than this does no harm.
|
||||
* As for the duration, **20 seconds** is enough time for the device to power on and start transmitting data.
|
||||
* As for the duration, **20 seconds** is enough time for the device to power on and start transmitting data.
|
||||
|
||||
Now try with the popular baud rates with both the suspected pins and try to compare the results. If you find any readable text with one of the pins and the text makes some sense then that’s the TX pin.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
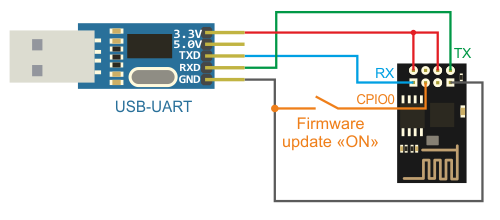
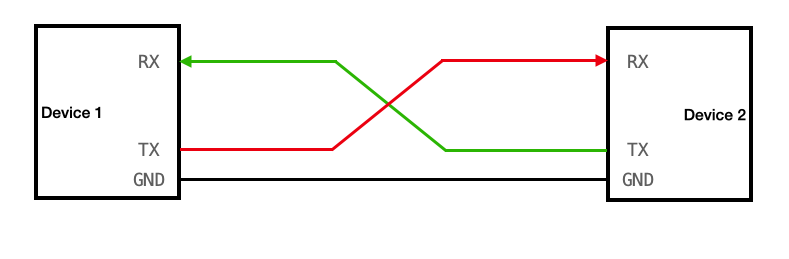
## Connect to serial port
|
||||
|
||||
### WARNING
|
||||
|
||||
It's not a big deal if you confuse the UART RX and TX ports with each other, because you can easily swap the wires connecting to them without any consequences. But confusing the VCC with the GND and connecting wires to them incorrectly **might fry the circuit**.
|
||||
|
||||
### Examples
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Connection using a USB to TTL
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -145,7 +143,6 @@ Under Ubuntu or Debian, a non-root user cannot have access to serial ports such
|
|||
* Ubuntu or Debian: `sudo usermod -a -G dialout $USER`
|
||||
* Arch-based: `sudo usermod -a -G uucp $USER`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Detect the baud rate
|
||||
|
||||
#### Most common baud rate
|
||||
|
|
@ -154,7 +151,6 @@ The most common baud rates for UART are `9600`, `19200`, `38400`, `57600` and `1
|
|||
|
||||
A table of other used but less common baud rates can be found here: [Here](https://lucidar.me/en/serialib/most-used-baud-rates-table/)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Autodetect the baud rate using a script
|
||||
|
||||
* [devttys0/baudrate.py](https://github.com/devttys0/baudrate/blob/master/baudrate.py)
|
||||
|
|
@ -170,7 +166,6 @@ pip2.7 install serial
|
|||
python2.7 baudrate.py -p /dev/ttyUSB0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Using PulseView
|
||||
|
||||
It is possible to get baudrate using the duration of a bit periode, using PulseView or any other bus analysis tools :
|
||||
|
|
@ -227,18 +222,17 @@ The closest common baudrate is : 115200. Configure the decoder and you should se
|
|||
uart1> bridge
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## UART over BLE
|
||||
|
||||
It’s an emulation of serial port over BLE. The UUID of the Nordic UART Service is `6E400001-B5A3-F393-E0A9-E50E24DCCA9E`. This service exposes two characteristics: one for transmitting and one for receiving.
|
||||
|
||||
* **RX Characteristic (UUID: 6E400002-B5A3-F393-E0A9-E50E24DCCA9E)** :
|
||||
* The peer can send data to the device by writing to the RX Characteristic of the service. ATT Write Request or ATT Write Command can be used. The received data is sent on the UART interface.
|
||||
* The peer can send data to the device by writing to the RX Characteristic of the service. ATT Write Request or ATT Write Command can be used. The received data is sent on the UART interface.
|
||||
* **TX Characteristic (UUID: 6E400003-B5A3-F393-E0A9-E50E24DCCA9E)** :
|
||||
* If the peer has enabled notifications for the TX Characteristic, the application can send data to the peer as notifications. The application will transmit all data received over UART as notifications.
|
||||
* If the peer has enabled notifications for the TX Characteristic, the application can send data to the peer as notifications. The application will transmit all data received over UART as notifications.
|
||||
|
||||
## References
|
||||
|
||||
### Examples
|
||||
* [nRF UART 2.0 - Nordic Semiconductor ASA](https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.nordicsemi.nrfUARTv2)
|
||||
* [UART/Serial Port Emulation over BLE](https://infocenter.nordicsemi.com/index.jsp?topic=%2Fcom.nordic.infocenter.sdk5.v14.0.0%2Fble_sdk_app_nus_eval.html)
|
||||
* [UART Over Bluetooth Low Energy](https://thejeshgn.com/2016/10/01/uart-over-bluetooth-low-energy/)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue