|
|
||
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| images | ||
| README.md | ||
| dist_android-zoo_27e283e2789e690dd97b264d41bd18e1ba2741d0 (1).zip | ||
README.md
Android Zoo
Who knew pigeons could use Android phones?
This sus pigeon stored the flag on 2 phones, and the flag format is SEE{:<gesture_pattern>}.
For example, if the password is password and the gesture pattern is 1337, the flag is SEE{password:1337}
Hint: Don't worry, the password is in rockyou!
Side note: why aren't there any pigeons in zoos?
About the Challenge
We were given a zip file that contains 2 folders called first_devices and second_devices. And in these folders there is information related to the device such as the device name, then there is a kind of file containing passwords and so on. And our goal is to get the password of the two devices
How to Solve?
Lets see the first_device folder first
If you open device_policies.xml, you will see the length of the password is 5
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8' standalone='yes' ?>
<policies setup-complete="true">
<active-password quality="65536" length="5" uppercase="0" lowercase="0" letters="0" numeric="0" symbols="0" nonletter="0" />
</policies>
And then I tried to find an information about cracking gatekeeper.pattern.key and I found this website
As you can see, because the length of the password is 5, I created a file called num.txt that contains all combination of the password. For example:
00000
00001
00002
...
And then I tried using Python code on the website to find the password of the first device.
# -*- coding=utf-8 -*-
import struct
import binascii
import scrypt
N = 16384;
r = 8;
p = 1;
current_index = 1
f=open('gatekeeper.pattern.key', 'rb')
blob = f.read()
s = struct.Struct('<'+'17s 8s 32s')
(meta, salt, signature) = s.unpack_from(blob)
f1=open('num.txt','r')
lines=f1.readlines()
lines.reverse()
for data in lines:
password=data.strip()
to_hash = meta
to_hash += password.encode(encoding='utf-8')
hash = scrypt.hash(to_hash, salt, N, r, p)
print ('{} {} <= {} => {}'.format(password, signature.hex(),(hash[0:32] == signature), hash[0:32].hex()))
current_index = current_index+1
if hash[0:32] == signature:
print ("[OK] Password is %s", password )
exit()
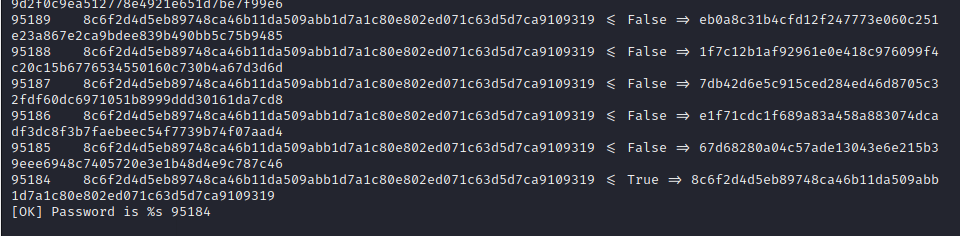
Wait until the program stops, and as you can see the password is 95184
After I got the first password, now lets check the second folder
If you open device_policies.xml, you will see the length of the password is 11 (3 uppercase, 7 lowercase, and 1 numeric)
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8' standalone='yes' ?>
<policies setup-complete="true">
<active-password quality="327680" length="11" uppercase="3" lowercase="7" letters="10" numeric="1" symbols="0" nonletter="1" />
</policies>
And then I tried to find an information about cracking password.key and I found this website
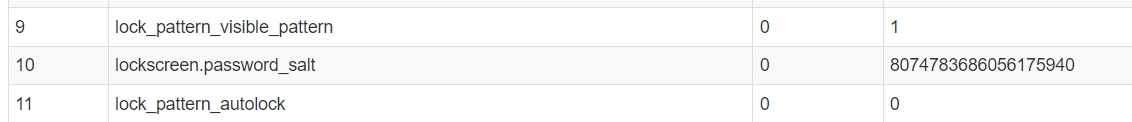
We need to parse locksettings.db file first to get the salt
And then if you open password.key you will see this string
6DFE4D0C832761398B38D7CFAD64D78760DEBAD266EB31BD62AFE3E486004CE6ECEC885C
When I read the blog find that the hexadecimal string of 72 bytes corresponds to the concatenation of the sha1(password + salt) and the md5(password + salt). And in the end, we got this information
6DFE4D0C832761398B38D7CFAD64D78760DEBAD2 = SHA1
66EB31BD62AFE3E486004CE6ECEC885C = MD5
8074783686056175940 = salt
Convert the salt first
printf "%x\n" 8074783686056175940
Store the hash using below format into a file called hash.txt
66EB31BD62AFE3E486004CE6ECEC885C$700f64fafd7f6944
And then run john using this command
john -form=dynamic='md5($p.$s)' --wordlist=/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt hash.txt
The password is PIGeon4ever
SEE{PIGeon4ever:95184}